配置
命令行选项
Locust 主要通过命令行参数进行配置。
$ locust --help
Usage: locust [options] [UserClass ...]
Common options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-f <filename>, --locustfile <filename>
The Python file or module that contains your test,
e.g. 'my_test.py'. Accepts multiple comma-separated
.py files, a package name/directory or a url to a
remote locustfile. Defaults to 'locustfile'.
--config <filename> File to read additional configuration from. See https:
//docs.locust.io/en/stable/configuration.html#configur
ation-file
-H <base url>, --host <base url>
Host to load test, in the following format:
https://www.example.com
-u <int>, --users <int>
Peak number of concurrent Locust users. Primarily used
together with --headless or --autostart. Can be
changed during a test by keyboard inputs w, W (spawn
1, 10 users) and s, S (stop 1, 10 users)
-r <float>, --spawn-rate <float>
Rate to spawn users at (users per second). Primarily
used together with --headless or --autostart
-t <time string>, --run-time <time string>
Stop after the specified amount of time, e.g. (300s,
20m, 3h, 1h30m, etc.). Only used together with
--headless or --autostart. Defaults to run forever.
-l, --list Show list of possible User classes and exit
--config-users [CONFIG_USERS ...]
User configuration as a JSON string or file. A list of
arguments or an Array of JSON configuration may be
provided
Web UI options:
--web-host <ip> Host to bind the web interface to. Defaults to '*'
(all interfaces)
--web-port <port number>, -P <port number>
Port on which to run web host
--headless Disable the web interface, and start the test
immediately. Use -u and -t to control user count and
run time
--autostart Starts the test immediately (like --headless, but
without disabling the web UI)
--autoquit <seconds> Quits Locust entirely, X seconds after the run is
finished. Only used together with --autostart. The
default is to keep Locust running until you shut it
down using CTRL+C
--web-login Protects the web interface with a login page. See
https://docs.locust.io/en/stable/extending-
locust.html#authentication
--tls-cert <filename>
Optional path to TLS certificate to use to serve over
HTTPS
--tls-key <filename> Optional path to TLS private key to use to serve over
HTTPS
--class-picker Enable select boxes in the web interface to choose
from all available User classes and Shape classes
--web-base-path WEB_BASE_PATH
Base path for the web interface (e.g., '/locust').
Default is empty (root path).
Master options:
Options for running a Locust Master node when running Locust distributed. A Master node need Worker nodes that connect to it before it can run load tests.
--master Launch locust as a master node, to which worker nodes
connect.
--master-bind-host <ip>
IP address for the master to listen on, e.g
'192.168.1.1'. Defaults to * (all available
interfaces).
--master-bind-port <port number>
Port for the master to listen on. Defaults to 5557.
--expect-workers <int>
Delay starting the test until this number of workers
have connected (only used in combination with
--headless/--autostart).
--expect-workers-max-wait <int>
How long should the master wait for workers to connect
before giving up. Defaults to wait forever
--enable-rebalancing Re-distribute users if new workers are added or
removed during a test run. Experimental.
Worker options:
Options for running a Locust Worker node when running Locust distributed.
Typically ONLY these options (and --locustfile) need to be specified on workers, since other options (-u, -r, -t, ...) are controlled by the master node.
--worker Set locust to run in distributed mode with this
process as worker. Can be combined with setting
--locustfile to '-' to download it from master.
--processes <int> Number of times to fork the locust process, to enable
using system. Combine with --worker flag or let it
automatically set --worker and --master flags for an
all-in-one-solution. Not available on Windows.
Experimental.
--master-host <hostname>
Hostname of locust master node to connect to. Defaults
to 127.0.0.1.
--master-port <port number>
Port to connect to on master node. Defaults to 5557.
Tag options:
Locust tasks can be tagged using the @tag decorator. These options let specify which tasks to include or exclude during a test.
-T [<tag> ...], --tags [<tag> ...]
List of tags to include in the test, so only tasks
with at least one matching tag will be executed
-E [<tag> ...], --exclude-tags [<tag> ...]
List of tags to exclude from the test, so only tasks
with no matching tags will be executed
Request statistics options:
--csv <filename> Store request stats to files in CSV format. Setting
this option will generate three files:
<filename>_stats.csv, <filename>_stats_history.csv and
<filename>_failures.csv. Any folders part of the
prefix will be automatically created
--csv-full-history Store each stats entry in CSV format to
_stats_history.csv file. You must also specify the '--
csv' argument to enable this.
--print-stats Enable periodic printing of request stats in UI runs
--only-summary Disable periodic printing of request stats during
--headless run
--reset-stats Reset statistics once spawning has been completed.
Should be set on both master and workers when running
in distributed mode
--html <filename> Store HTML report to file path specified
--json Prints the final stats in JSON format to stdout.
Useful for parsing the results in other
programs/scripts. Use together with --headless and
--skip-log for an output only with the json data.
Logging options:
--skip-log-setup Disable Locust's logging setup. Instead, the
configuration is provided by the Locust test or Python
defaults.
--loglevel <level>, -L <level>
Choose between DEBUG/INFO/WARNING/ERROR/CRITICAL.
Default is INFO.
--logfile <filename> Path to log file. If not set, log will go to stderr
Other options:
--show-task-ratio Print table of the User classes' task execution ratio.
Use this with non-zero --user option if some classes
define non-zero fixed_count attribute.
--show-task-ratio-json
Print json data of the User classes' task execution
ratio. Use this with non-zero --user option if some
classes define non-zero fixed_count attribute.
--version, -V Show program's version number and exit
--exit-code-on-error <int>
Sets the process exit code to use when a test result
contain any failure or error. Defaults to 1.
-s <number>, --stop-timeout <number>
Number of seconds to wait for a simulated user to
complete any executing task before exiting. Default is
to terminate immediately. When running distributed,
this only needs to be specified on the master.
--equal-weights Use equally distributed task weights, overriding the
weights specified in the locustfile.
User classes:
<UserClass1 UserClass2>
At the end of the command line, you can list User
classes to be used (available User classes can be
listed with --list). LOCUST_USER_CLASSES environment
variable can also be used to specify User classes.
Default is to use all available User classes
Examples:
locust -f my_test.py -H https://www.example.com
locust --headless -u 100 -t 20m --processes 4 MyHttpUser AnotherUser
See documentation for more details, including how to set options using a file or environment variables: https://docs.locust.io/en/stable/configuration.html环境变量
选项也可以通过环境变量进行设置。它们通常与命令行参数相同,但需要大写并以 LOCUST_ 为前缀:
在 Linux/macOS 上:
$ LOCUST_LOCUSTFILE=custom_locustfile.py locust在 Windows 上:
> set LOCUST_LOCUSTFILE=custom_locustfile.py
> locust配置文件
选项也可以通过配置文件设置,支持配置文件格式为 config 或 TOML 格式。
Locust 默认会查找 ~/.locust.conf、./locust.conf 和 ./pyproject.toml。你可以使用 --config 标志指定一个额外的配置文件。
locust --config custom_config.conf下面是 Locust 配置文件的最小化示例:
稍后在本文中查看所有可用的配置选项。
locust.conf
locustfile = locust_files/my_locust_file.py
headless = true
host = https://target-system
run-time = 1m
spawn-rate =
users = 1以下是 Locust 支持的配置文件示例:
locust.conf
locustfile = locust_files/my_locust_file.py
headless = true
master = true
expect-workers = 5
host = https://target-system
users = 100
spawn-rate = 10
run-time = 10m
tags = [Critical, Normal]pyproject.toml
使用 TOML 文件时,配置选项应当定义在 [tool.locust] 部分。
[tool.locust]
locustfile = "locust_files/my_locust_file.py"
headless = true
master = true
expect-workers = 5
host = "https://target-system"
users = 100
spawn-rate = 10
run-time = "10m"
tags = ["Critical", "Normal"]|
配置值的读取(并覆盖)顺序如下: |
所有可用的配置选项
这是所有可用配置选项及其对应的命令行、环境变量和配置文件键的表格:
| 命令行 | 环境 | 配置文件 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
-f, --locustfile |
LOCUST_LOCUSTFILE |
locustfile |
包含测试的 Python 文件或模块,例如 ‘my_test.py’。支持多个逗号分隔的 .py 文件、包名/目录或远程 locustfile 的 URL。默认为 ‘locustfile’。 |
-H, --host |
LOCUST_HOST |
host |
需要进行负载测试的主机,格式为:https://www.example.com |
-u, --users |
LOCUST_USERS |
users |
最大并发 Locust 用户数。通常与 –headless 或 –autostart 一起使用。可以通过键盘输入 w, W(增加 1, 10 个用户)和 s, S(停止 1, 10 个用户)来更改测试期间的用户数。 |
-r, --spawn-rate |
LOCUST_SPAWN_RATE |
spawn-rate |
用户的生成速率(每秒生成多少用户)。通常与 –headless 或 –autostart 一起使用。 |
-t, --run-time |
LOCUST_RUN_TIME |
run-time |
在指定的时间后停止,例如(300s, 20m, 3h, 1h30m 等)。仅与 –headless 或 –autostart 一起使用。默认为永远运行。 |
--config-users |
LOCUST_CONFIG_USERS |
config-users |
用户配置,作为 JSON 字符串或文件。可以提供参数列表或 JSON 配置数组。 |
--web-host |
LOCUST_WEB_HOST |
web-host |
绑定 web 界面的主机。默认为 ‘*’(所有接口)。 |
--web-port, -P |
LOCUST_WEB_PORT |
web-port |
运行 web 主机的端口。 |
--headless |
LOCUST_HEADLESS |
headless |
禁用 web 界面,并立即开始测试。使用 -u 和 -t 来控制用户数和运行时间。 |
--autostart |
LOCUST_AUTOSTART |
autostart |
立即开始测试(与 –headless 相似,但不禁用 web UI)。 |
--autoquit |
LOCUST_AUTOQUIT |
autoquit |
测试结束后 X 秒退出 Locust。仅与 –autostart 一起使用。默认情况下,Locust 会保持运行,直到通过 CTRL+C 关闭。 |
--web-login |
LOCUST_WEB_LOGIN |
web-login |
保护 web 界面,要求登录才能访问。参见 https://docs.locust.io/en/stable/extending-locust.html#authentication |
--tls-cert |
LOCUST_TLS_CERT |
tls-cert |
用于通过 HTTPS 提供服务的 TLS 证书的路径(可选)。 |
--tls-key |
LOCUST_TLS_KEY |
tls-key |
用于通过 HTTPS 提供服务的 TLS 私钥的路径(可选)。 |
--class-picker |
LOCUST_USERCLASS_PICKER |
class-picker |
启用 web 界面中的选择框,供选择所有可用的用户类和形状类。 |
--master |
LOCUST_MODE_MASTER |
master |
启动 Locust 作为主节点,工作节点将连接到该节点。 |
--master-bind-host |
LOCUST_MASTER_BIND_HOST |
master-bind-host |
主节点监听的 IP 地址,例如 ‘192.168.1.1’。默认为 *(所有可用接口)。 |
--master-bind-port |
LOCUST_MASTER_BIND_PORT |
master-bind-port |
主节点监听的端口。默认为 5557。 |
--expect-workers |
LOCUST_EXPECT_WORKERS |
expect-workers |
等待该数量的工作节点连接后才开始测试(仅与 –headless/–autostart 一起使用)。 |
--expect-workers-max-wait |
LOCUST_EXPECT_WORKERS_MAX_WAIT |
expect-workers-max-wait |
主节点等待工作节点连接的最大时间。默认为永远等待。 |
--worker |
LOCUST_MODE_WORKER |
worker |
设置 Locust 在分布式模式下运行,将此进程作为工作节点。可以结合设置 –locustfile 为 ‘-’ 从主节点下载配置文件。 |
--processes |
LOCUST_PROCESSES |
processes |
启动多个 Locust 进程的次数,以启用系统。与 –worker 标志结合使用,或让其自动设置 –worker 和 –master 标志以实现一体化解决方案。仅在 Windows 上不可用。实验性功能。 |
--master-host |
LOCUST_MASTER_NODE_HOST |
master-host |
连接的 Locust 主节点的主机名。默认为 127.0.0.1。 |
--master-port |
LOCUST_MASTER_NODE_PORT |
master-port |
连接到主节点的端口。默认为 5557。 |
--web-base-path |
LOCUST_WEB_BASE_PATH |
web-base-path |
Web 界面的基础路径(例如 ‘/locust’)。默认为空(根路径)。 |
-T, --tags |
LOCUST_TAGS |
tags |
测试中要包括的标签列表,只有至少有一个匹配标签的任务才会执行。 |
-E, --exclude-tags |
LOCUST_EXCLUDE_TAGS |
exclude-tags |
要从测试中排除的标签列表,只有没有匹配标签的任务才会执行。 |
--csv |
LOCUST_CSV |
csv |
将请求统计信息存储为 CSV 格式的文件。启用此选项将生成三个文件:<filename>_stats.csv、<filename>_stats_history.csv 和 <filename>_failures.csv。任何文件夹路径都会自动创建。 |
--csv-full-history |
LOCUST_CSV_FULL_HISTORY |
csv-full-history |
将每个统计条目存储为 CSV 格式,存储在 _stats_history.csv 文件中。必须同时指定 ‘–csv’ 参数来启用此选项。 |
--print-stats |
LOCUST_PRINT_STATS |
print-stats |
在 UI 运行期间定期打印请求统计信息。 |
--only-summary |
LOCUST_ONLY_SUMMARY |
only-summary |
在 –headless 运行期间禁用定期打印请求统计信息。 |
--reset-stats |
LOCUST_RESET_STATS |
reset-stats |
在生成用户后重置统计信息。在分布式模式下运行时,应在主节点和工作节点上设置此选项。 |
--html |
LOCUST_HTML |
html |
将 HTML 报告存储到指定的文件路径。 |
--skip-log-setup |
LOCUST_SKIP_LOG_SETUP |
skip-log-setup |
禁用 Locust 的日志设置。相反,配置由 Locust 测试或 Python 默认提供。 |
--loglevel, -L |
LOCUST_LOGLEVEL |
loglevel |
选择日志级别:DEBUG/INFO/WARNING/ERROR/CRITICAL。默认值为 INFO。 |
--logfile |
LOCUST_LOGFILE |
logfile |
日志文件路径。如果未设置,日志将输出到 stderr。 |
--exit-code-on-error |
LOCUST_EXIT_CODE_ON_ERROR |
exit-code-on-error |
设置测试结果包含任何失败或错误时的进程退出码。默认值为 1。 |
-s, --stop-timeout |
LOCUST_STOP_TIMEOUT |
stop-timeout |
等待模拟用户完成正在执行的任务的秒数,直到退出。默认情况下立即终止。如果在分布式模式下运行,仅在主节点上需要指定此选项。 |
不显示 web UI 运行
请参见 在没有 web 界面的情况下运行
一次使用多个 locustfile
-f/--locustfile 接受多个用逗号分隔的 locustfile。
示例:
在以下文件结构中:
├── locustfiles/
│ ├── locustfile1.py
│ ├── locustfile2.py
│ └── more_files/
│ ├── locustfile3.py
│ ├── _ignoreme.py执行:
locust -f locustfiles/locustfile1.py,locustfiles/locustfile2.py,locustfiles/more_files/locustfile3.pyLocust 将使用 locustfile1.py、locustfile2.py 和 more_files/locustfile3.py。
此外,-f/--locustfile 也接受目录作为选项。Locust 会递归地搜索指定目录中的 *.py 文件,并忽略以“_”开头的文件。
示例:
locust -f locustfilesLocust 将使用 locustfile1.py、locustfile2.py 和 more_files/locustfile3.py。
你还可以使用 -f/--locustfile 指定 Web URL。这将下载该文件并像普通的 locustfile 一样使用它。
示例:
locust -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/locustio/locust/master/examples/basic.py从 UI 中选择用户类、形状和任务
你可以通过 --class-picker 标志在 WebUI 中选择要运行的 Shape 类和 User 类。如果没有选择,将使用所有可用的 User 类。
例如,假设文件结构如下:
├── src/
│ ├── some_file.py
├── locustfiles/
│ ├── locustfile1.py
│ ├── locustfile2.py
│ └── more_files/
│ ├── locustfile3.py
│ ├── _ignoreme.py
│ └── shape_classes/
│ ├── DoubleWaveShape.py
│ ├── StagesShape.py执行:
locust -f locustfiles --class-pickerWeb UI 将显示:
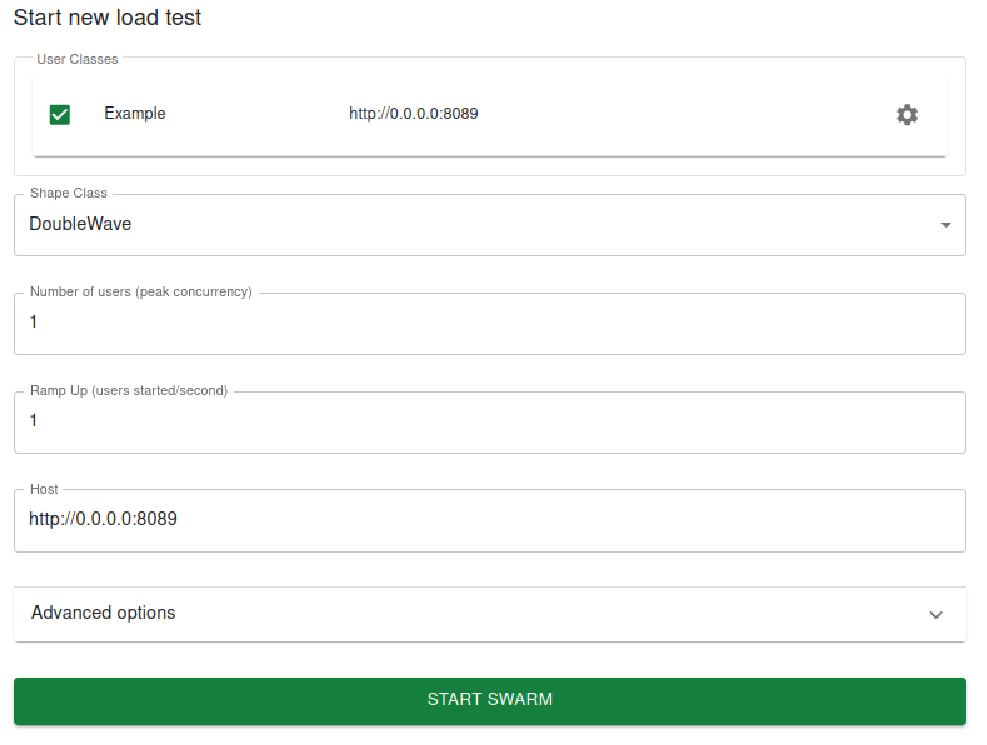
类选择器还允许禁用单个 User 任务、改变权重或固定数量,并配置主机。
你甚至可以添加自定义属性,使其对每个 User 可配置。只需为你的 User 添加一个 json 类方法:
class Example(HttpUser):
@task
def example_task(self):
self.client.get(f"/example/{self.some_custom_arg}")
@classmethod
def json(self):
return {
"host": self.host,
"some_custom_arg": "example"
}从命令行配置用户
你也可以通过命令行更新 User 类的属性,使用 --config-users 参数:
locust --config-users '{"user_class_name": "Example", "fixed_count": 1, "some_custom_attribute": false}'要配置多个用户,可以将多个参数传递给 --config-users,或者使用 JSON 数组。你也可以传递一个指向 JSON 文件的路径:
locust --config-users '{"user_class_name": "Example", "fixed_count": 1}' '{"user_class_name": "ExampleTwo", "fixed_count": 2}'
locust --config-users '[{"user_class_name": "Example", "fixed_count": 1}, {"user_class_name": "ExampleTwo", "fixed_count": 2}]'
locust --config-users my_user_config.json使用这种方式配置用户时,你可以设置任何属性。
|
|
自定义参数
参见 自定义参数。
自定义统计设置
Locust 统计信息的默认配置是在 stats.py 文件的常量中设置的。你可以通过覆盖这些值来调整它以满足特定的需求。要做到这一点,导入 locust.stats 模块并覆盖所需的设置:
import locust.stats
locust.stats.CONSOLE_STATS_INTERVAL_SEC = 15你可以直接在 Locust 文件中进行此操作,或者将其提取到一个单独的文件中,以供所有 Locust 文件共享。
可以修改的统计参数列表是:
参数名称 |
目的 |
STATS_NAME_WIDTH |
控制请求名称列在控制台输出中的宽度 |
STATS_TYPE_WIDTH |
控制请求类型列在控制台输出中的宽度 |
CSV_STATS_INTERVAL_SEC |
配置时,指定 CSV 文件写入的时间间隔 |
CONSOLE_STATS_INTERVAL_SEC |
控制结果写入控制台的时间间隔 |
CURRENT_RESPONSE_TIME_PERCENTILE_WINDOW |
计算当前响应时间百分位数时使用的窗口大小/分辨率(单位:秒) |
PERCENTILES_TO_REPORT |
要计算并报告的响应时间百分位数列表 |
PERCENTILES_TO_CHART |
在 UI 图表中显示的响应时间百分位数列表 |
PERCENTILES_TO_STATISTICS |
在 UI 统计信息中显示的响应时间百分位数列表 |