登录表单配置
快速入门
理解了入门案例之后,接下来我们再来看一下登录表单的详细配置。
首先创建一个新的 Spring Boot 项目,引入 Web 和 Spring Security 依赖,代码如下:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>项目创建好之后,为了方便测试,需要在 application.properties 中添加如下配置,将登录用户名和密码固定下来:
spring.security.user.name=javaboy
spring.security.user.password=123接下来,我们在 resources/static 目录下创建一个 login.html 页面,这个是我们自定义的登录页面:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>登录</title>
<link href="//maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.1/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet" id="bootstrap-css">
<script src="//maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.1/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
<script src="//cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/jquery/3.2.1/jquery.min.js"></script>
</head>
<style>
#login .container #login-row #login-column #login-box {
border: 1px solid #9C9C9C;
background-color: #EAEAEA;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="login">
<div class="container">
<div id="login-row" class="row justify-content-center align-items-center">
<div id="login-column" class="col-md-6">
<div id="login-box" class="col-md-12">
<form id="login-form" class="form" action="/doLogin" method="post">
<h3 class="text-center text-info">登录</h3>
<div th:text="${SPRING_SECURITY_LAST_EXCEPTION}"></div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="username" class="text-info">用户名:</label><br>
<input type="text" name="uname" id="username" class="form-control">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="password" class="text-info">密码:</label><br>
<input type="text" name="passwd" id="password" class="form-control">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<input type="submit" name="submit" class="btn btn-info btn-md" value="登录">
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>这个 logint.html 中的核心内容就是一个登录表单,登录表单中有三个需要注意的地方:
-
form 的 action,这里给出的是 /doLogin,表示表单要提交到 /doLogin 接口上。
-
用户名输入框的 name 属性值为 uname,当然这个值是可以自定义的,这里采用了 uname。
-
密码输入框的 name 属性值为 passwd, passwd 也是可以自定义的。
login.html 定义好之后,接下来定义两个测试接口,作为受保护的资源。 当用户登录成功后, 就可以访问到受保护的资源。 接口定义如下:
@RestController
public class LoginController {
@RequestMapping("/index")
public String index() {
return "login success";
}
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "hello spring security";
}
}最后再提供一个 Spring Security 的配置类:
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login.html")
.loginProcessingUrl("/doLogin")
.defaultSuccessUrl("/index ")
.failureUrl("/login.html")
.usernameParameter("uname")
.passwordParameter("passwd")
.permitAll()
.and()
.csrf().disable();
}
}在 Spring Security 中,如果我们需要自定义配置,基本上都是继承自 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 来实现的,当然 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 本身的配置还是比较复杂, 同时也是比较丰富的,这里先不做过多的展开, 仅就结合上面的代码来解释,在下一个小节中我们将会对这里的配置再做更加详细的介绍。
-
首先 configure 方法中是一个链式配置,当然也可以不用链式配置,每一个属性配置完毕后再从 http. 重新开始写起。
-
authorizeRequests() 方法表示开启权限配置(该方法的含义其实比较复杂,我们在 13.4.4 小节还会再次介绍该方法),.anyRequest().authenticated() 表示所有的请求都要认证之后才能访问。
-
有的读者会对 and() 方法表示疑惑,and() 方法会返回 HttpSecurityBuilder 对象的一个子类(实际上就是 HttpSecurity),所以 and() 方法相当于又回到 HttpSecurity 实例,重新开启新一轮的配置。如果觉得 and() 方法很难理解,也可以不用 and() 方法,在 .anyRequest().authenticated() 配置完成后直接用分号(;) 结束,然后通过 http.formLogin() 继续配置表单登录。
-
formLogin() 表示开启表单登录配置,loginPage 用来配置登录页面地址;loginProcessingUrl 用来配置登录接口地址; defaultSuccessUrl 表示登录成功后的跳转地址;failureUrl 表示登录失败后的跳转地址;usernameParameter 表示登录用户名的参数名称;passwordParameter 表示登录密码的参数名称;permitAll 表示跟登录相关的页面和接口不做拦截,直接通过。需要注意的是,loginProcessingUrl、 usernameParameter、passwordParameter 需要和 login.html 中登录表单的配置一致。
-
最后的 csrf().disable() 表示禁用 CSRF 防御功能,Spring Security 自带了 CSRF 防御机制,但是我们这里为了测试方便,先将 CSRF 防御机制关闭,本书第 9 章将会详细介绍 CSRF 攻击与防御问题。
配置完成后,启动 Spring Boot 项目,浏览器地址栏中输入 http://localhost:8080/index ,会自动跳转到 http://localhost:8080/login.html 页面,如图 2-5 所示。 输入用户名和密码进行登录(用户名为 javaboy,密码为 123),登录成功之后,就可以访问到 index 页面了,如图 2-6 所示。

经过上面的配置,我们已经成功自定义了一个登录页面出来,用户在登录成功之后,就可以访问受保护的资源了。
配置细节
当然, 前面的配置比较粗糙,这里还有一些配置的细节需要和读者分享一下。 在前面的配置中,我们用 defaultSuccessUrl 表示用户登录成功后的跳转地址,用 failureUrl 表示用户登录失败后的跳转地址。关于登录成功和登录失败,除了这两个方法可以配置之外,还有另外两个方法也可以配置。
登录成功
当用户登录成功之后,除了 defaultSuccessUrl 方法可以实现登录成功后的跳转之外,successForwardUrl 也可以实现登录成功后的跳转, 代码如下:
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login.html")
.loginProcessingUrl("/doLogin")
.successForwardUrl("/index ")
.failureUrl("/login.html")
.usernameParameter("uname")
.passwordParameter("passwd")
.permitAll()
.and()
.csrf().disable();
}
}defaultSuccessUrl 和 successForwardUrl 的区别如下:
-
defaultSuccessUrl 表示当用户登录成功之后,会自动重定向到登录之前的地址上,如果用户本身就是直接访问的登录页面,则登录成功后就会重定向到 defaultSuccessUrl 指定的页面中。例如,用户在未认证的情况下,访问了 /hello 页面,此时会自动重定向到登录页面, 当用户登录成功后,就会自动重定向到 /hello 页面;而用户如果一开始就访问登录页面,则登录成功后就会自动重定向到 defaultSuccessUrl 所指定的页面中。
-
successForwardUrl 则不会考虑用户之前的访问地址,只要用户登录成功,就会通过服务器端跳转到 successForwardUrl 所指定的页面。
-
defaultSuccessUrl 有一个重载方法,如果重载方法的第二个参数传入 true,则 defaultSuccessUrl 的效果与 successForwardUrl 类似,即不考虑用户之前的访问地址,只要登录成功,就重定向到 defaultSuccessUrl 所指定的页面。不同之处在于,defaultSuccessUrl 是通过重定向实现的跳转(客户端跳转), 而 successForwardUrl 则是通过服务器端跳转实现的。
无论是 defaultSuccessUrl 还是 successForwardUrl,最终所配置的都是 AuthenticationSuccessHandler 接口的实例。 Spring Security 中专门提供了 AuthenticationSuccessHandler 接口用来处理登录成功事项:
public interface AuthenticationSuccessHandler {
default void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain,
Authentication authentication)
throws IOException, ServletException {
onAuthenticationSuccess(request, response, authentication);
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
Authentication authentication)
throws IOException, ServletException;
}由上述代码可以看到,AuthenticationSuccessHandler 接口中一共定义了两个方法,其中一个是 default 方法,此方法是 Spring Security 5.2 开始加入进来的,在处理特定的认证请求 Authentication Filter 中会用到;另外一个非 default 方法, 则用来处理登录成功的具体事项,其中 request 和 response 参数好理解,authentication 参数保存了登录成功的用户信息。我们将在后面的章节中详细介绍 authentication 参数。
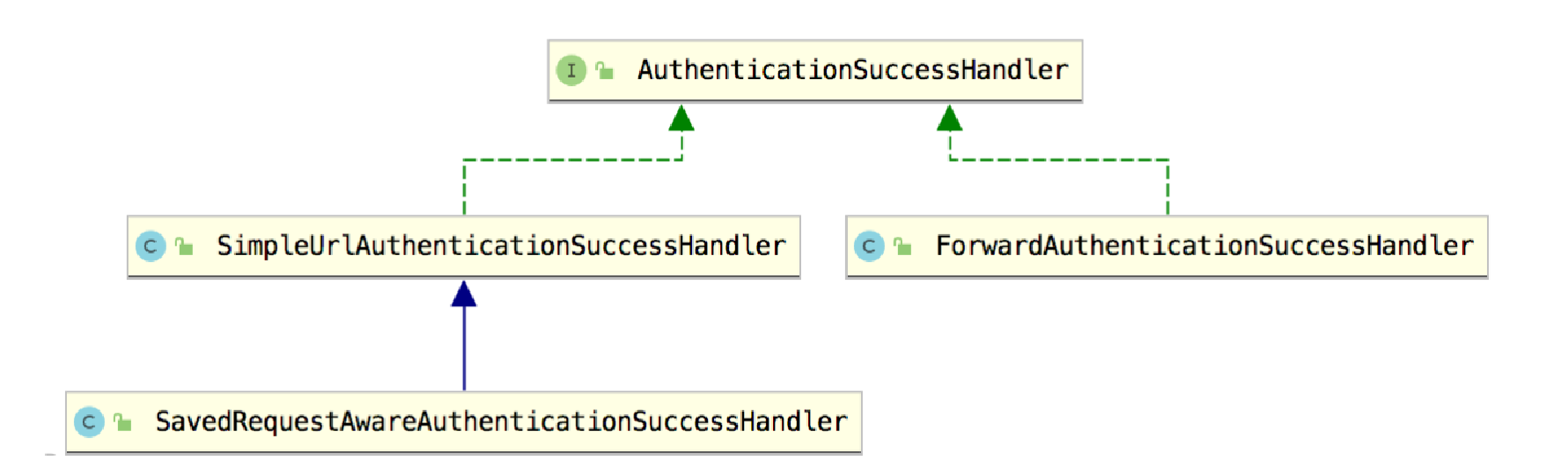
AuthenticationSuccessHandler 接口共有三个实现类,如图 2-7 所示。
-
SimpleUrlAuthenticationSuccessHandler 继承自 AbstractAuthenticationTargetUrlRequestHandler,通过 AbstractAuthenticationTargetUrlRequestHandler 中的 handle 方法实现请求重定向。
-
SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler 在 SimpleUrlAuthenticationSuccessHandler 的基础上增加了请求缓存的功能,可以记录之前请求的地址,进而在登录成功后重定向到一开始访问的地址。
-
ForwardAuthenticationSuccessHandler 的实现则比较容易,就是一个服务端跳转。
我们来重点分析 SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler 和 ForwardAuthenticationSuccessHandler 的实现。
当通过 defaultSuccessUrl 来设置登录成功后重定向的地址时,实际上对应的实现类就是 SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler,由于该类的源码比较长,这里列出来一部分核心代码:
public class SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler extends
SimpleUrlAuthenticationSuccessHandler {
private RequestCache requestCache = new HttpSessionRequestCache();
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
Authentication authentication)
throws ServletException, IOException {
SavedRequest savedRequest = requestCache.getRequest(request, response);
if (savedRequest == null) {
super.onAuthenticationSuccess(request, response, authentication);
return;
}
String targetUrlParameter = getTargetUrlParameter();
if (isAlwaysUseDefaultTargetUrl()
|| (targetUrlParameter != null && StringUtils.hasText(request
.getParameter(targetUrlParameter)))) {
requestCache.removeRequest(request, response);
super.onAuthenticationSuccess(request, response, authentication);
return;
}
clearAuthenticationAttributes(request);
String targetUrl = savedRequest.getRedirectUrl();
getRedirectStrategy().sendRedirect(request, response, targetUrl);
}
public void setRequestCache(RequestCache requestCache) {
this.requestCache = requestCache;
}
}这里的核心方法就是 onAuthenticationSuccess:
-
首先从 requestCache 中获取缓存下来的请求,如果没有获取到缓存请求,就说明用户在访问登录页面之前并没有访问其他页面,此时直接调用父类的 onAuthenticationSuccess 方法来处理,最终会重定向到 defaultSuccessUrl 指定的地址。
-
接下来会获取一个 targetUrlParameter,这个是用户显式指定的、 希望登录成功后重定向的地址,例如用户发送的登录请求是 http://localhost:8080/doLogin?target=/hello ,这就表示当用户登录成功之后,希望自动重定向到 /hello 这个接口。 getTargetUrlParameter 就是要获取重定向地址参数的 key,也就是上面的 target,拿到 target 之后,就可以获取到重定向地址了。
-
如果 targetUrlParameter 存在,或者用户设置了 alwaysUseDefaultTargetUrl 为 true,这个时候缓存下来的请求就没有意义了。此时会直接调用父类的 onAuthenticationSuccess 方法完成重定向。 targetUrlParameter 存在,则直接重定向到 targetUrlParameter 指定的地址;alwaysUseDefaultTargetUrl 为 true,则直接重定向到 defaultSuccessUrl 指定的地址;如果 targetUrlParameter 存在并且 alwaysUseDefaultTargetUrl 为 true,则重定向到 defaultSuccessUrl 指定的地址。
-
如果前面的条件都不满足,那么最终会从缓存请求 savedRequest 中获取重定向地址,然后进行重定向操作。
这就是 SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler 的实现逻辑,开发者也可以配置自己的 SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler, 代码如下:
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login.html")
.loginProcessingUrl("/doLogin")
.successHandler(successHandler()) // 替代 defaultSuccessUrl,用户自定义
.failureUrl("/login.html")
.usernameParameter("uname")
.passwordParameter("passwd")
.permitAll()
.and()
.csrf().disable();
}
SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler successHandler() {
SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler handler =
new SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler();
handler.setDefaultTargetUrl("/index");
handler.setTargetUrlParameter("target");
return handler;
}
}注意在配置时指定了 targetUrlParameter 为 target,这样用户就可以在登录请求中,通过 target 来指定跳转地址了,然后我们修改一下前面 login.html 中的 form 表单:
<form id="login-form" class="form" action="/doLogin?target=/hello" method="post">
<h3 class="text-center text-info">登录</h3>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="username" class="text-info">用户名:</label><br>
<input type="text" name="uname" id="username" class="form-control">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="password" class="text-info">密码:</label><br>
<input type="text" name="passwd" id="password" class="form-control">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<input type="submit" name="submit" class="btn btn-info btn-md" value="登录">
</div>
</form>在 form 表单中,action 修改为 /doLogin?target=/hello,这样当用户登录成功之后,就始终跳转到 /hello 接口了。
当我们通过 successForwardUrl 来设置登录成功后重定向的地址时,实际上对应的实现类就是 ForwardAuthenticationSuccessHandler, ForwardAuthenticationSuccessHandler 的源码特别简 单,就是一个服务端转发,代码如下:
public class ForwardAuthenticationSuccessHandler
implements AuthenticationSuccessHandler {
private final String forwardUrl;
public ForwardAuthenticationSuccessHandler(String forwardUrl) {
this.forwardUrl = forwardUrl;
}
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
Authentication authentication)
throws IOException, ServletException {
request.getRequestDispatcher(forwardUrl).forward(request, response);
}
}由上述代码可以看到,主要功能就是调用 getRequestDispatcher 方法进行服务端转发。
AuthenticationSuccessHandler 默认的三个实现类,无论是哪一个,都是用来处理页面跳转的。有时候页面跳转并不能满足我们的需求,特别是现在流行的前后端分离开发中,用户登录成功后,就不再需要页面跳转了,只需要给前端返回一个 JSON 数据即可,告诉前端登录成功还是登录失败,前端收到消息之后自行处理。像这样的需求,我们可以通过自定义 AuthenticationSuccessHandler 的实现类来完成:
public class MyAuthenticationSuccessHandler implements
AuthenticationSuccessHandler {
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
Authentication authentication)
throws IOException, ServletException {
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
Map<String, Object> resp = new HashMap<>();
resp.put("status", 200);
resp.put("msg", "登录成功!");
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
String s = om.writeValueAsString(resp);
response.getWriter().write(s);
}
}在自定义的 MyAuthenticationSuccessHandler 中,重写 onAuthenticationSuccess 方法,在该方法中,通过 HttpServletResponse 对象返回一段登录成功的 JSON 字符串给前端即可。最后,在 SecurityConfig 中配置自定义的 MyAuthenticationSuccessHandler, 代码如下:
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login.html")
.loginProcessingUrl("/doLogin")
.successHandler(new MyAuthenticationSuccessHandler())
.failureUrl("/login.html")
.usernameParameter("uname")
.passwordParameter("passwd")
.permitAll()
.and()
.csrf().disable();
}
}配置完成后,重启项目。此时,当用户成功登录之后,就不会进行页面跳转了,而是返回一段 JSON 字符串。
登录失败
接下来看登录失败的处理逻辑。为了方便在前端页面展示登录失败的异常信息,我们首先在项目的 pom.xml 文件中引入 thymeleaf 依赖,代码如下:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>然后在 resources/templates 目录下新建 mylogin.html,代码如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>登录</title>
<link href="//cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@4.6.2/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet" id="bootstrap-css">
<script src="//cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/jquery/3.2.1/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script src="//cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@4.6.2/dist/js/bootstrap.bundle.min.js"></script>
</head>
<style>
#login .container #login-row #login-column #login-box {
border: 1px solid #9C9C9C;
background-color: #EAEAEA;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="login">
<div class="container">
<div id="login-row" class="row justify-content-center align-items-center">
<div id="login-column" class="col-md-6">
<div id="login-box" class="col-md-12">
<form id="login-form" class="form" action="/doLogin" method="post">
<h3 class="text-center text-info">登录</h3>
<div th:text="${SPRING_SECURITY_LAST_EXCEPTION}"></div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="username" class="text-info">用户名:</label><br>
<input type="text" name="uname" id="username" class="form-control">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="password" class="text-info">密码:</label><br>
<input type="text" name="passwd" id="password" class="form-control">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<input type="submit" name="submit" class="btn btn-info btn-md" value="登录">
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>mylogin.html 和前面的 login.html 基本类似,前面的 login.html 是静态页面,这里的 mylogin.html 是 thymeleaf 模板页面,mylogin.html 页面在 form 中多了一个 div,用来展示登录失败时候的异常信息,登录失败的异常信息会放在 request 中返回到前端,开发者可以将其直接提取出来展示。
既然 mylogin.html 是动态页面,就不能像静态页面那样直接访问了,需要我们给 mylogin.html 页面提供一个访问控制器:
@Controller
public class MyLoginController {
@RequestMapping("/mylogin.html")
public String mylogin() {
return "mylogin";
}
}最后再在 SecurityConfig 中配置登录页面, 代码如下:
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/mylogin.html")
.loginProcessingUrl("/doLogin")
.defaultSuccessUrl("/index.html")
.failureUrl("/mylogin.html")
.usernameParameter("uname")
.passwordParameter("passwd")
.permitAll()
.and()
.csrf().disable();
}
}failureUrl 表示登录失败后重定向到 mylogin.html 页面。 重定向是一种客户端跳转,重定向不方便携带请求失败的异常信息(只能放在 URL 中)。
如果希望能够在前端展示请求失败的异常信息,可以使用下面这种方式:
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/mylogin.html")
.loginProcessingUrl("/doLogin")
.defaultSuccessUrl("/index.html")
.failureForwardUrl("/mylogin.html")
.usernameParameter("uname")
.passwordParameter("passwd")
.permitAll()
.and()
.csrf().disable();
}
}failureForwardUrl 方法从名字上就可以看出,这种跳转是一种服务器端跳转,服务器端跳转的好处是可以携带登录异常信息。如果登录失败,自动跳转回登录页面后, 就可以将错误信息展示出来,如图 2-8 所示。

无论是 failureUrl 还是 failureForwardUrl,最终所配置的都是 AuthenticationFailureHandler 接口的实现。 Spring Security 中提供了 AuthenticationFailureHandler 接口, 用来规范登录失败的实现:
public interface AuthenticationFailureHandler {
void onAuthenticationFailure(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException exception)
throws IOException, ServletException;
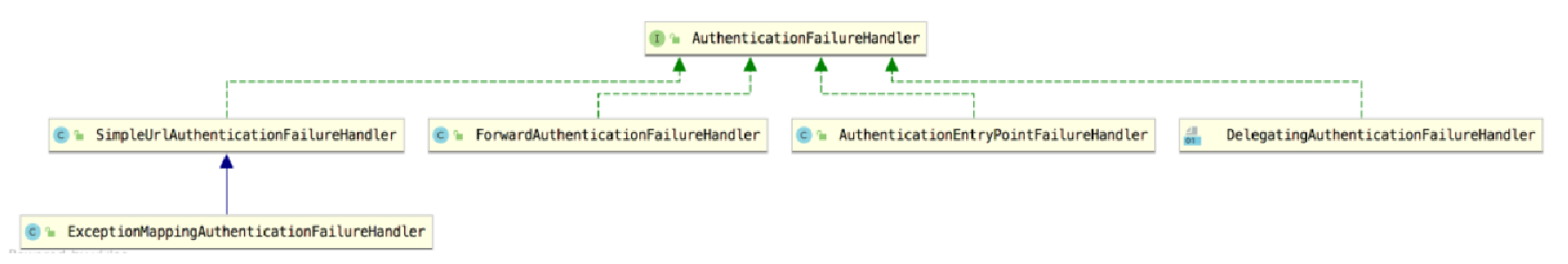
}AuthenticationFailureHandler 接口中只有一个 onAuthenticationFailure 方法, 用来处理登录失败请求, request 和 response 参数很好理解,最后的 exception 则表示登录失败的异常信息。Spring Security 中为 AuthenticationFailureHandler 一共提供了五个实现类,如图 2-9 所示。
-
SimpleUrlAuthenticationFailureHandler 默认的处理逻辑就是通过重定向跳转到登录页面,当然也可以通过配置 forwardToDestination 属性将重定向改为服务器端跳转, failureUrl 方法的底层实现逻辑就是 SimpleUrlAuthenticationFailureHandler。
-
ExceptionMappingAuthenticationFailureHandler 可以实现根据不同的异常类型,映射到不同的路径。
-
ForwardAuthenticationFailureHandler 表示通过服务器端跳转来重新回到登录页面,failureForwardUrl 方法的底层实现逻辑就是 ForwardAuthenticationFailureHandler。
-
AuthenticationEntryPointFailureHandler 是 Spring Security 5.2 新引进的处理类,可以通过 AuthenticationEntryPoint 来处理登录异常。
-
DelegatingAuthenticationFailureHandler 可以实现为不同的异常类型配置不同的登录失败处理回调。
这里举一个简单的例子。假如不使用 failureForwardUrl 方法,同时又想在登录失败后通过服务器端跳转回到登录页面,那么可以自定义 SimpleUrlAuthenticationFailureHandler 配置,并将 forwardToDestination 属性设置为 true, 代码如下:
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/mylogin.html")
.loginProcessingUrl("/doLogin")
.defaultSuccessUrl("/index.html")
.failureHandler(failureHandler())
.usernameParameter("uname")
.passwordParameter("passwd")
.permitAll()
.and()
.csrf().disable();
}
SimpleUrlAuthenticationFailureHandler failureHandler() {
SimpleUrlAuthenticationFailureHandler handler =
new SimpleUrlAuthenticationFailureHandler("/mylogin.html");
handler.setUseForward(true);
return handler;
}
}这样配置之后,如果用户再次登录失败,就会通过服务端跳转重新回到登录页面,登录页面也会展示相应的错误信息,效果和 failureForwardUrl 一致。
SimpleUrlAuthenticationFailureHandler 的源码也很简单,我们一起来看一下实现逻辑(源码比较长,这里列出来核心部分):
public class SimpleUrlAuthenticationFailureHandler implements
AuthenticationFailureHandler {
private String defaultFailureUrl;
private boolean forwardToDestination = false;
private boolean allowSessionCreation = true;
private RedirectStrategy redirectStrategy = new DefaultRedirectStrategy();
public SimpleUrlAuthenticationFailureHandler() {
}
public SimpleUrlAuthenticationFailureHandler(String defaultFailureUrl) {
setDefaultFailureUrl(defaultFailureUrl);
}
public void onAuthenticationFailure(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException exception)
throws IOException, ServletException {
if (defaultFailureUrl == null) {
response.sendError(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED.value(),
HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED.getReasonPhrase());
} else {
saveException(request, exception);
if (forwardToDestination) {
request.getRequestDispatcher(defaultFailureUrl)
.forward(request, response);
} else {
redirectStrategy
.sendRedirect(request, response, defaultFailureUrl);
}
}
}
protected final void saveException(HttpServletRequest request,
AuthenticationException exception) {
if (forwardToDestination) {
request
.setAttribute(WebAttributes.AUTHENTICATION_EXCEPTION, exception);
} else {
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null || allowSessionCreation) {
request.getSession()
.setAttribute(WebAttributes.AUTHENTICATION_EXCEPTION,
exception);
}
}
}
public void setUseForward(boolean forwardToDestination) {
this.forwardToDestination = forwardToDestination;
}
}从这段源码中可以看到,当用户构造 SimpleUrlAuthenticationFailureHandler 对象的时候,就传入了 defaultFailureUrl,也就是登录失败时要跳转的地址。 在 onAuthenticationFailure 方法中,如果发现 defaultFailureUrl 为 null,则直接通过 response 返回异常信息,否则调用 saveException 方法。 在 saveException 方法中,如果 forwardToDestination 属性设置为 true,表示通过服务器端跳转回到登录页面,此时就把异常信息放到 request 中。再回到 onAuthenticationFailure 方法中,如果用户设置了 forwardToDestination 为 true,就通过服务器端跳转回到登录页面,否则通过重定向回到登录页面。
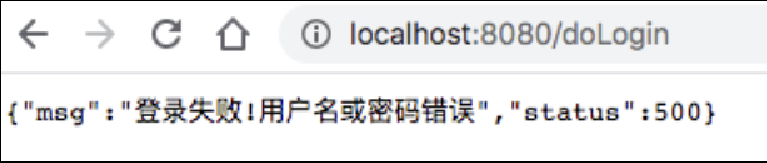
如果是前后端分离开发,登录失败时就不需要页面跳转了,只需要返回 JSON 字符串给前端即可,此时可以通过自定义 AuthenticationFailureHandler 的实现类来完成, 代码如下:
public class MyAuthenticationFailureHandler implements
AuthenticationFailureHandler {
@Override
public void onAuthenticationFailure(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
AuthenticationException exception)
throws IOException, ServletException {
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
Map<String, Object> resp = new HashMap<>();
resp.put("status", 500);
resp.put("msg", "登录失败!" + exception.getMessage());
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
String s = om.writeValueAsString(resp);
response.getWriter().write(s);
}
}然后在 SecurityConfig 中进行配置即可:
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/mylogin.html")
.loginProcessingUrl("/doLogin")
.defaultSuccessUrl("/index.html")
.failureHandler(new MyAuthenticationFailureHandler())
.usernameParameter("uname")
.passwordParameter("passwd")
.permitAll()
.and()
.csrf().disable();
}
}配置完成后,当用户再次登录失败,就不会进行页面跳转了,而是直接返回 JSON 字符串,如图 2-10 所示。
注销登录
Spring Security 中提供了默认的注销页面,当然开发者也可以根据自己的需求对注销登录进行定制。
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
//省略其他配置
.and()
.logout()
.logoutUrl("/logout")
.invalidateHttpSession(true)
.clearAuthentication(true)
.logoutSuccessUrl("/mylogin.html")
.and()
.csrf().disable();
}
}-
通过 .logout() 方法开启注销登录配置。
-
logoutUrl 指定了注销登录请求地址,默认是 GET 请求,路径为 /logout。
-
invalidateHttpSession 表示是否使 session 失效,默认为 true。
-
clearAuthentication 表示是否清除认证信息,默认为 true。
-
logoutSuccessUrl 表示注销登录后的跳转地址。
配置完成后,再次启动项目,登录成功后, 在浏览器中输入 http://localhost:8080/logout 就可以发起注销登录请求了。 注销成功后,会自动跳转到 mylogin.html 页面。
如果项目有需要,开发者也可以配置多个注销登录的请求,同时还可以指定请求的方法:
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
//省略其他配置
.and()
.logout()
.logoutRequestMatcher(new OrRequestMatcher(
new AntPathRequestMatcher("/logout1", "GET"),
new AntPathRequestMatcher("/logout2", "POST")))
.invalidateHttpSession(true)
.clearAuthentication(true)
.logoutSuccessUrl("/mylogin.html")
.and()
.csrf().disable();
}
}上面这个配置表示注销请求路径有两个:
-
第一个是 /logout1,请求方法是 GET。
-
第二个是 /logout2,请求方法是 POST。
使用任意一个请求都可以完成登录注销。
如果项目是前后端分离的架构,注销成功后就不需要页面跳转了,只需将注销成功的信息返回给前端即可,此时我们可以自定义返回内容:
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
//省略其他配置
.and()
.logout()
.logoutRequestMatcher(new OrRequestMatcher(
new AntPathRequestMatcher("/logout1", "GET"),
new AntPathRequestMatcher("/logout2", "POST")))
.invalidateHttpSession(true)
.clearAuthentication(true)
.logoutSuccessHandler((req,resp,auth)->{
resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();
result.put("status", 200);
result.put("msg", "注销成功!");
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
String s = om.writeValueAsString(result);
resp.getWriter().write(s);
})
.and()
.csrf().disable();
}
}配置 logoutSuccessHandler 和 logoutSuccessUrl 类似于前面所介绍的 successHandler 和 defaultSuccessUrl 之间的关系,只是类不同而已,因此这里不再赘述,读者可以按照我们前面的分析思路自行分析。
配置完成后,重启项目,登录成功后再去注销登录,无论是使用 /logout1 还是 /logout2 进行注销,只要注销成功后,就会返回一段 JSON 字符串。
如果开发者希望为不同的注销地址返回不同的结果,也是可以的,配置如下:
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
//省略其他配置
.and()
.logout()
.logoutRequestMatcher(new OrRequestMatcher(
new AntPathRequestMatcher("/logout1", "GET"),
new AntPathRequestMatcher("/logout2", "POST")))
.invalidateHttpSession(true)
.clearAuthentication(true)
.defaultLogoutSuccessHandlerFor((req,resp,auth)->{
resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();
result.put("status", 200);
result.put("msg", "使用 logout1 注销成功!");
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
String s = om.writeValueAsString(result);
resp.getWriter().write(s);
},new AntPathRequestMatcher("/logout1","GET"))
.defaultLogoutSuccessHandlerFor((req,resp,auth)->{
resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();
result.put("status", 200);
result.put("msg", "使用 logout2 注销成功!");
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
String s = om.writeValueAsString(result);
resp.getWriter().write(s);
},new AntPathRequestMatcher("/logout2","POST"))
.and()
.csrf().disable();
}
}通过 defaultLogoutSuccessHandlerFor 方法可以注册多个不同的注销成功回调函数,该方法第一个参数是注销成功回调,第二个参数则是具体的注销请求。当用户注销成功后,使用了哪个注销请求,就给出对应的响应信息。