使用Actuator MBean
默认情况下,所有的Actuator端点都会以MBeans的形式暴露。但是,从SpringBoot 2.2开始,JMX本身默认是被禁用的。要在Spring Boot应用程序中启用JMX,可以将spring.jmx.enabled设置为true。对于application.yml文件,设置方式如下所示:
spring:
jmx:
enabled: true设置了这个属性后,Spring对JMX的支持就会启用,Actuator的端点都会暴露为MBean。我们可以使用任意的JMX客户端连接Actuator端点的MBean。借助Java开发工具集中的JConsole,可以看到Actuator MBean列到了org.springframework.boot域下,如图17.1所示。
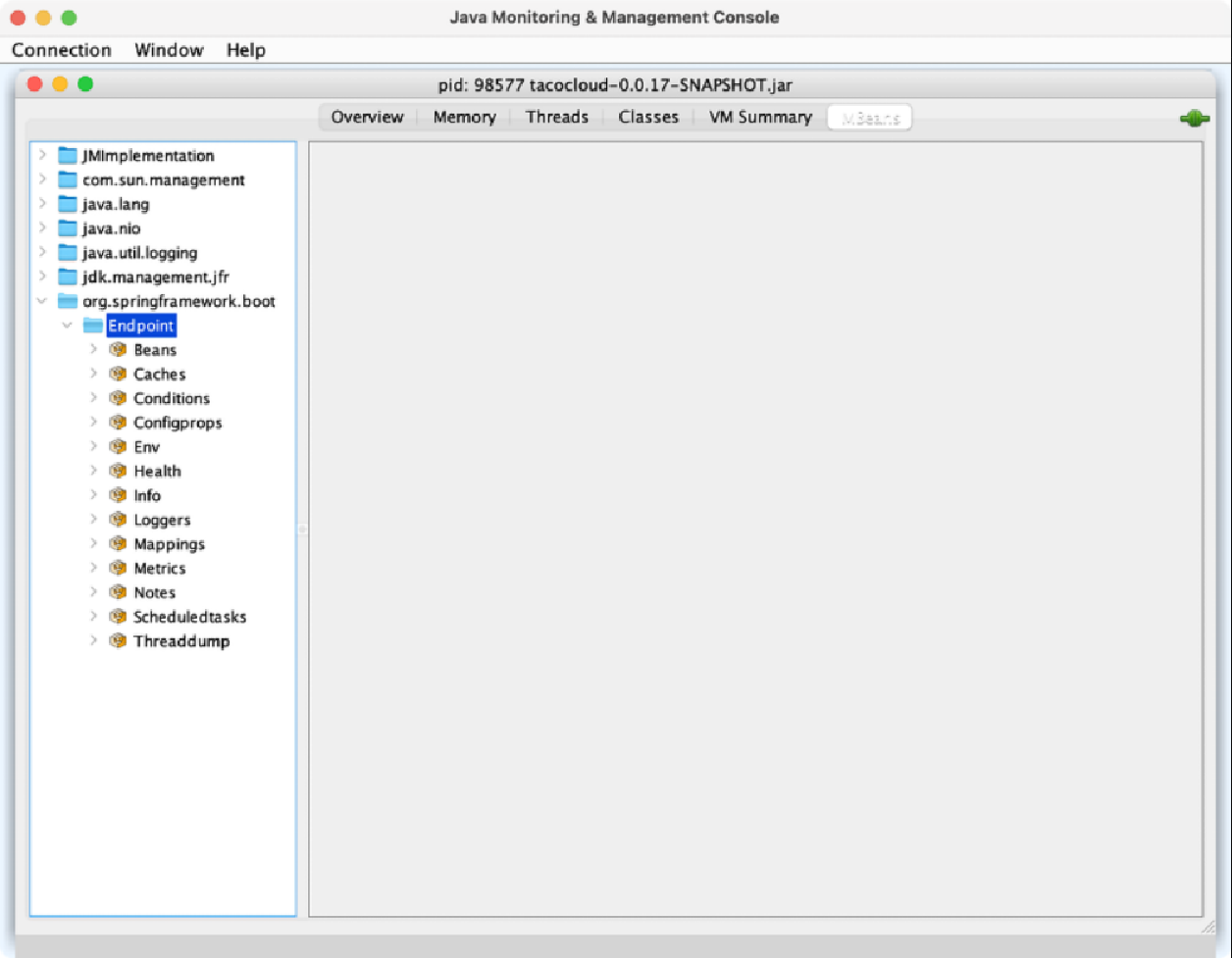
对于Actuator MBean端点,非常好的一点在于它们默认就是对外暴露的,我们没有必要明确声明要包含哪些MBean端点,但是对于HTTP端点,我们需要进行声明。可以通过设置management.endpoints.jmx.exposure.include和management.endpoints.jmx. exposure.exclude属性来缩小可选的范围。例如,我们想要限制Actuator MBean端点只暴露“/health”“/info”“/bean”和“/conditions”端点,那么可以按照如下的方式设置management.endpoints.jmx.exposure.include:
management:
endpoints:
jmx:
exposure:
include: health,info,bean,conditions如果只想排除其中的几个端点,可以按照如下的方式设置management.endpoints. jmx.exposure.exclude属性:
management:
endpoints:
jmx:
exposure:
exclude: env,metrics这里使用management.endpoints.jmx.exposure.exclude排除了“/env”和“/metrics”端点。所有其他Actuator端点依然会暴露为MBean。
要在JConsole中调用一个或多个Actuator MBean托管的操作,可以在左侧树中展开MBean端点,然后在Operations下选择所需的操作。
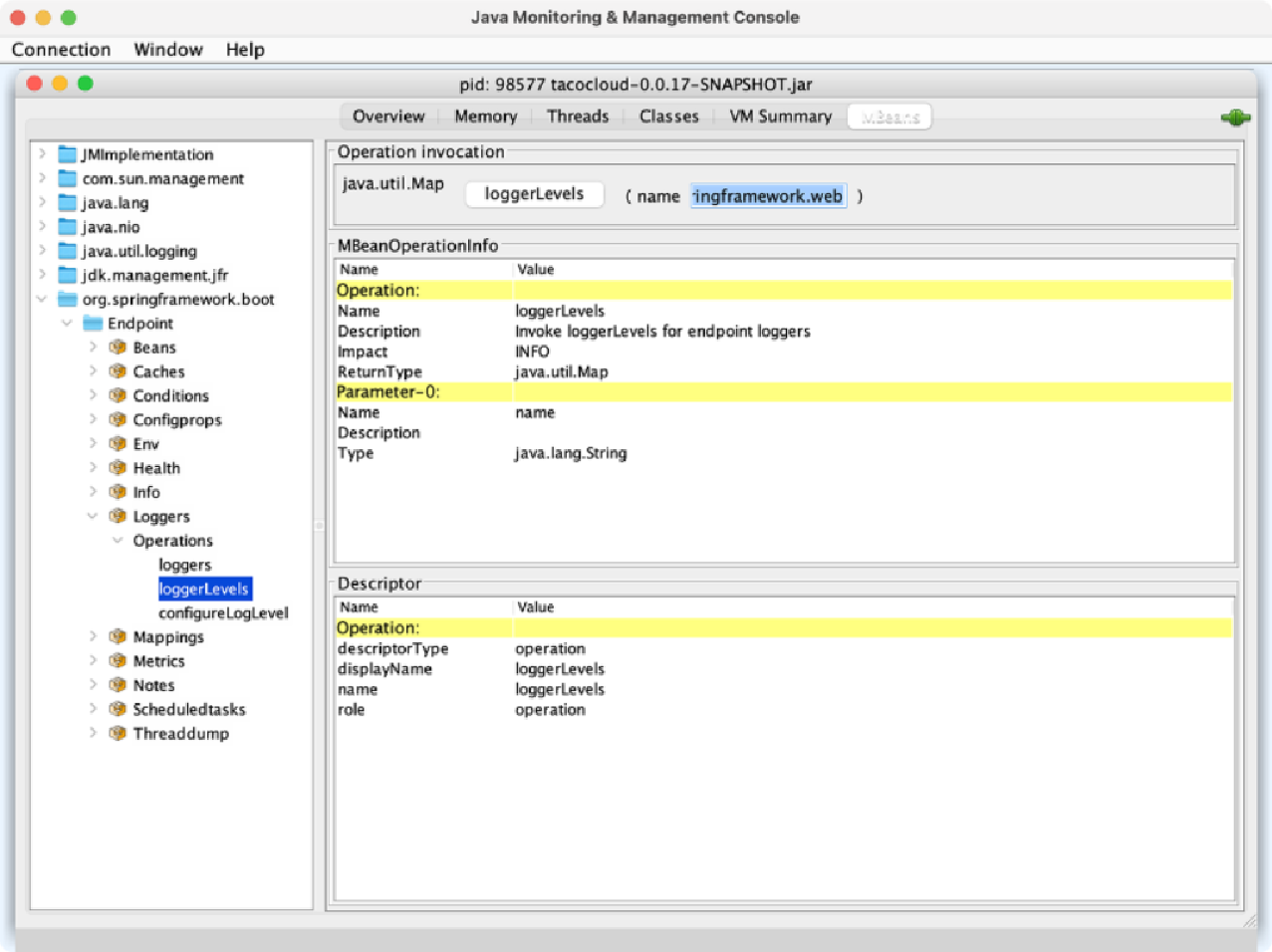
例如,如果想要探查tacos.ingredients包的日志级别,那么可以展开Loggers MBean并点击名为loggerLevels的操作,如图17.2所示。在右上方表单的Name文本域中输入包名(tacos.ingredients),然后点击loggerLevels按钮。
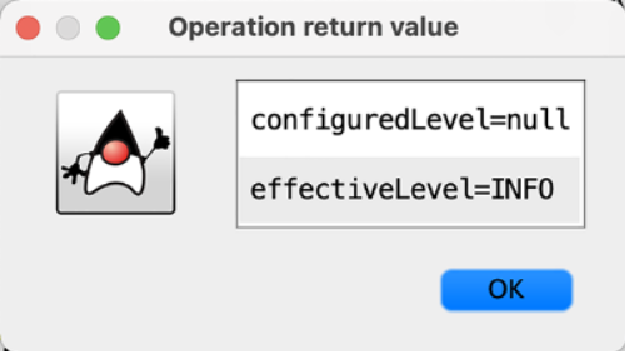
点击loggerLevels按钮后,弹出的对话框中会展现来自“/loggers”端点MBean的响应,大致如图17.3所示。
尽管JConsole UI使用起来有些麻烦,但是你应该可以掌握使用它的技巧并以相同的方式探索其他的Actuator端点。如果你不喜欢JConsole,也没有问题,有很多其他的JMX客户端可供选择。