模拟 API 请求
简介
Web API 通常作为 HTTP 接口实现。Playwright 提供了模拟和修改网络流量的 API,支持 HTTP 和 HTTPS。页面发出的任何请求,包括 XHR 和 fetch 请求,都可以被追踪、修改和模拟。Playwright 还允许使用包含多个网络请求的 HAR 文件来进行模拟。
模拟 API 请求
以下代码将拦截所有对 */**/api/v1/fruits 的请求,并返回自定义响应,而不会实际调用 API。测试会访问使用模拟路由的 URL,并断言页面上是否存在模拟数据。
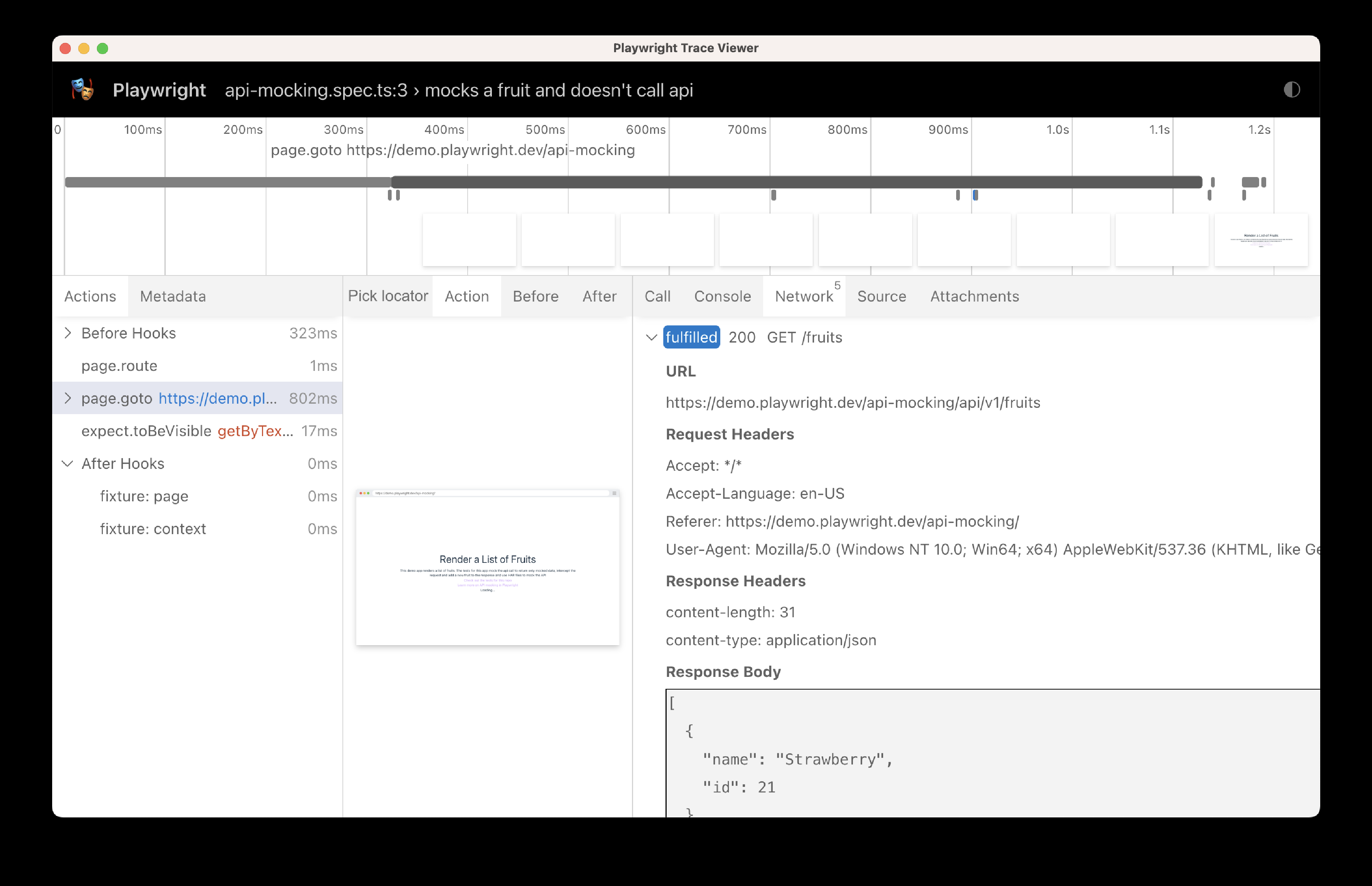
test("mocks a fruit and doesn't call api", async ({ page }) => {
// Mock the api call before navigating
await page.route('*/**/api/v1/fruits', async route => {
const json = [{ name: 'Strawberry', id: 21 }];
await route.fulfill({ json });
});
// Go to the page
await page.goto('https://demo.playwright.dev/api-mocking');
// Assert that the Strawberry fruit is visible
await expect(page.getByText('Strawberry')).toBeVisible();
});可以从测试的追踪中看到,API 并未被调用,而是使用了模拟数据。
阅读更多关于高级网络的信息。
修改 API 响应
有时需要发出 API 请求,但响应需要被修改以便进行可复现的测试。在这种情况下,可以先执行请求,然后将修改后的响应进行填充。
在下面的例子中,我们拦截了对水果 API 的请求,并将一个新水果 'Loquat' 添加到数据中。然后我们访问 URL,并断言数据是否存在:
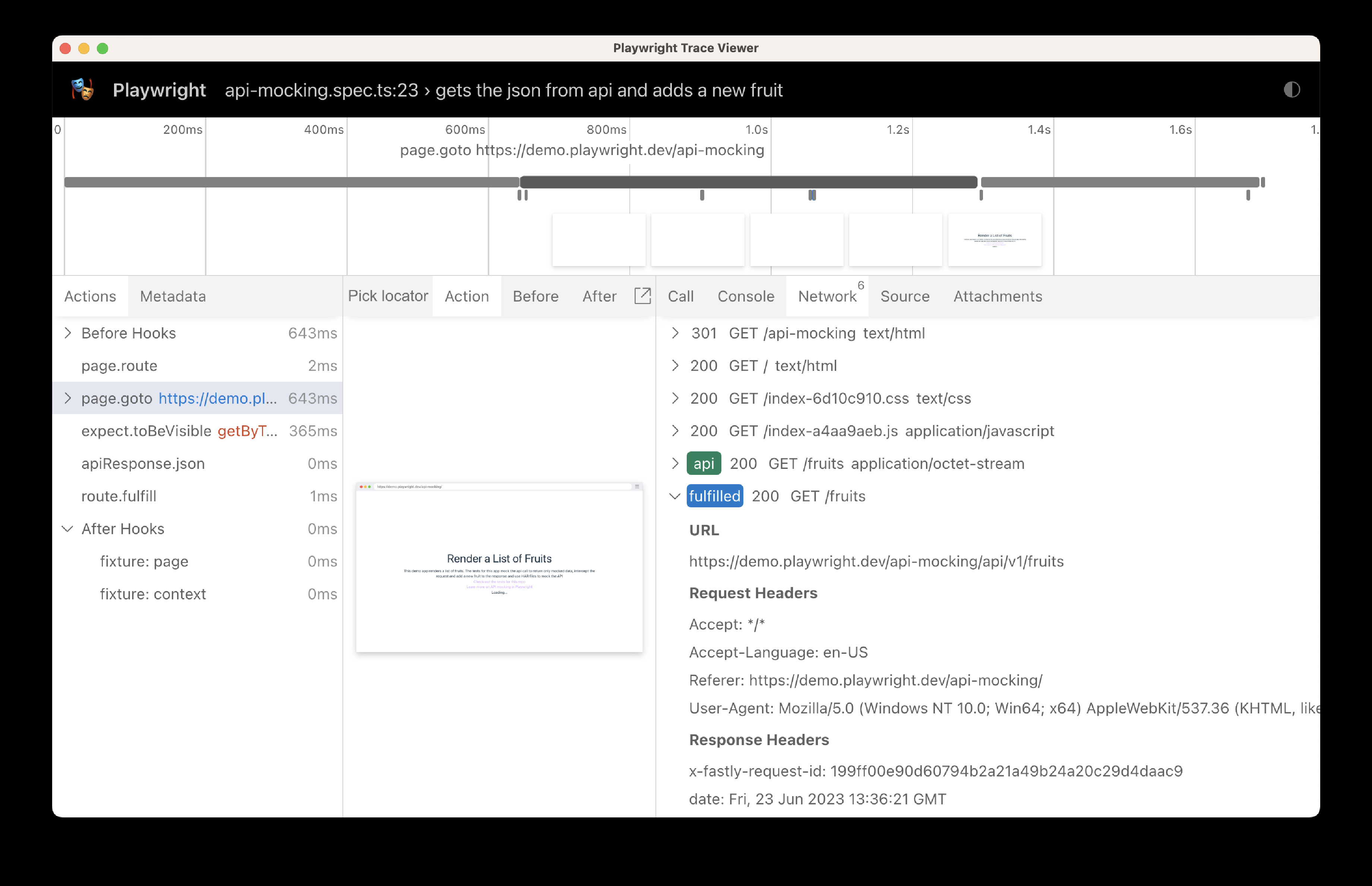
test('gets the json from api and adds a new fruit', async ({ page }) => {
// Get the response and add to it
await page.route('*/**/api/v1/fruits', async route => {
const response = await route.fetch();
const json = await response.json();
json.push({ name: 'Loquat', id: 100 });
// Fulfill using the original response, while patching the response body
// with the given JSON object.
await route.fulfill({ response, json });
});
// Go to the page
await page.goto('https://demo.playwright.dev/api-mocking');
// Assert that the new fruit is visible
await expect(page.getByText('Loquat', { exact: true })).toBeVisible();
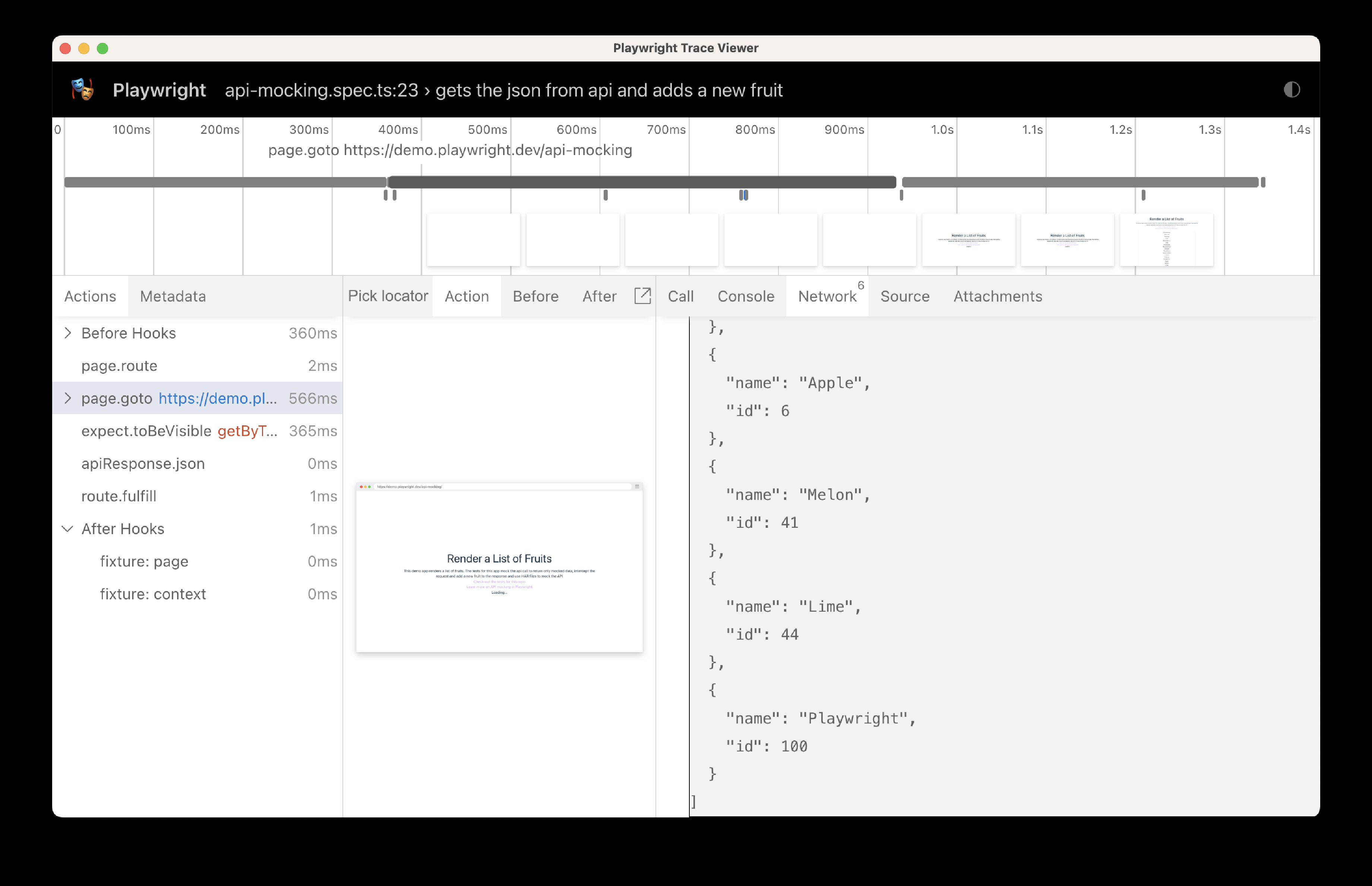
});通过测试的追踪可以看到,API 被调用且响应被修改。
通过检查响应,我们可以看到我们的新水果已经添加到列表中。
阅读更多关于高级网络的信息。
使用 HAR 文件进行模拟
HAR 文件(HTTP Archive 文件)记录了页面加载过程中所有网络请求的信息,包括请求和响应的头部、cookies、内容、时间等。可以使用 HAR 文件来模拟测试中的网络请求。你需要:
-
录制 HAR 文件。
-
将 HAR 文件和测试一起提交。
-
在测试中使用录制的 HAR 文件来路由请求。
录制 HAR 文件
要录制一个 HAR 文件,我们使用 page.routeFromHAR() 或 browserContext.routeFromHAR() 方法。这个方法需要传入 HAR 文件的路径和一个可选的配置对象。配置对象可以包含 URL,以便只有与指定的 glob 模式匹配的请求才会从 HAR 文件中提供。如果没有指定,所有请求都将从 HAR 文件中提供。
将 update 选项设置为 true 会使用实际的网络信息创建或更新 HAR 文件,而不是从 HAR 文件中提供请求。在创建测试并用真实数据填充 HAR 时,使用这个选项。
test('records or updates the HAR file', async ({ page }) => {
// Get the response from the HAR file
await page.routeFromHAR('./hars/fruit.har', {
url: '*/**/api/v1/fruits',
update: true,
});
// Go to the page
await page.goto('https://demo.playwright.dev/api-mocking');
// Assert that the fruit is visible
await expect(page.getByText('Strawberry')).toBeVisible();
});修改 HAR 文件
一旦你录制了一个 HAR 文件,你可以通过打开 "hars" 文件夹中的哈希 .txt 文件并编辑其中的 JSON 来修改它。这个文件应该被提交到你的源代码管理系统中。每次你使用 update: true 运行测试时,它会用 API 的请求更新你的 HAR 文件。
[
{
"name": "Playwright",
"id": 100
},
// ... other fruits
]从 HAR 文件回放
现在,录制并修改了 HAR 文件的模拟数据后,你可以在测试中使用它来提供匹配的响应。为此,只需关闭或移除 update 选项。这将使测试通过 HAR 文件运行,而不是直接调用 API。
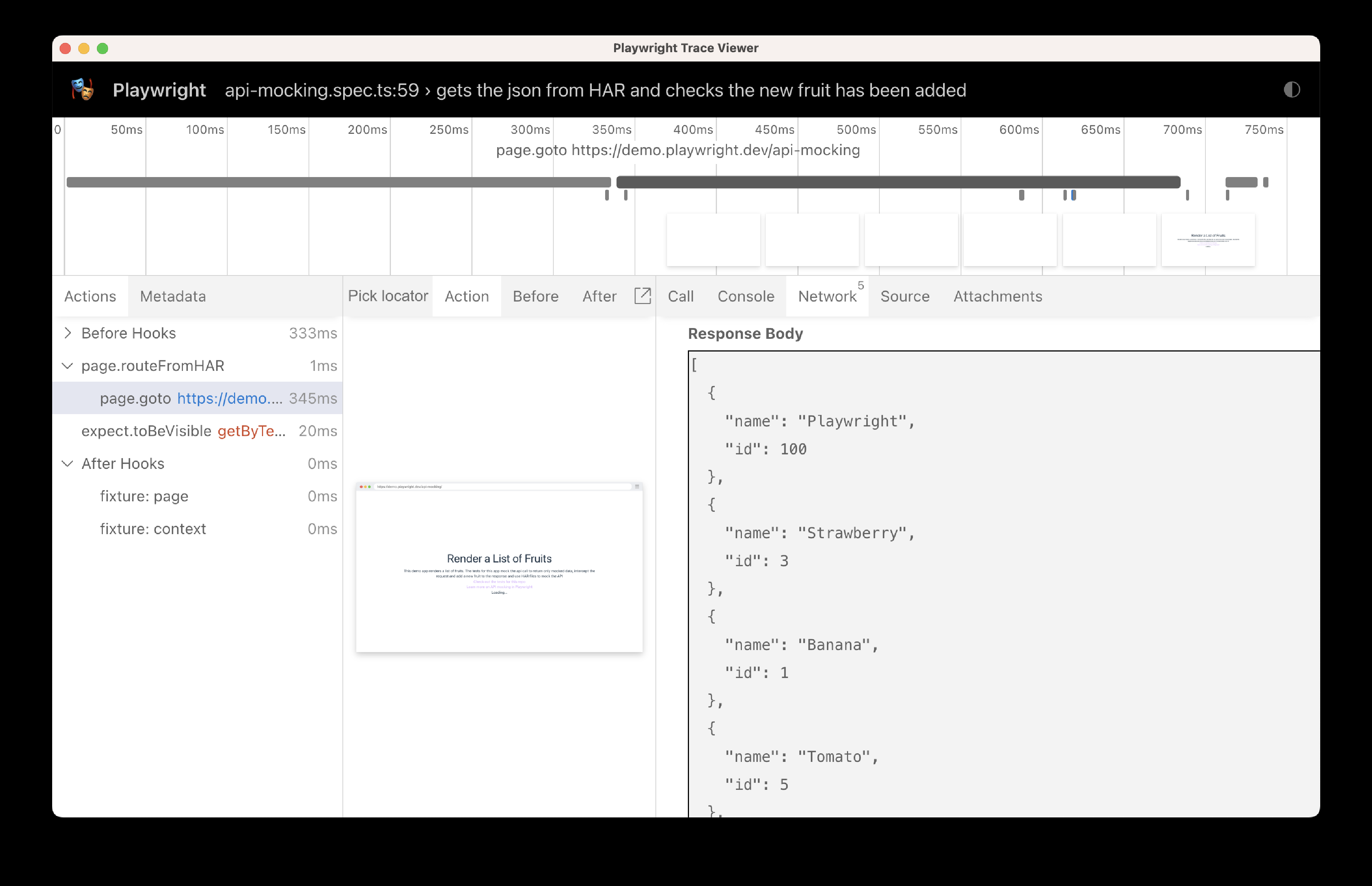
test('gets the json from HAR and checks the new fruit has been added', async ({ page }) => {
// Replay API requests from HAR.
// Either use a matching response from the HAR,
// or abort the request if nothing matches.
await page.routeFromHAR('./hars/fruit.har', {
url: '*/**/api/v1/fruits',
update: false,
});
// Go to the page
await page.goto('https://demo.playwright.dev/api-mocking');
// Assert that the Playwright fruit is visible
await expect(page.getByText('Playwright', { exact: true })).toBeVisible();
});在我们测试的跟踪中,可以看到路由是从 HAR 文件中提供的,而没有调用 API。
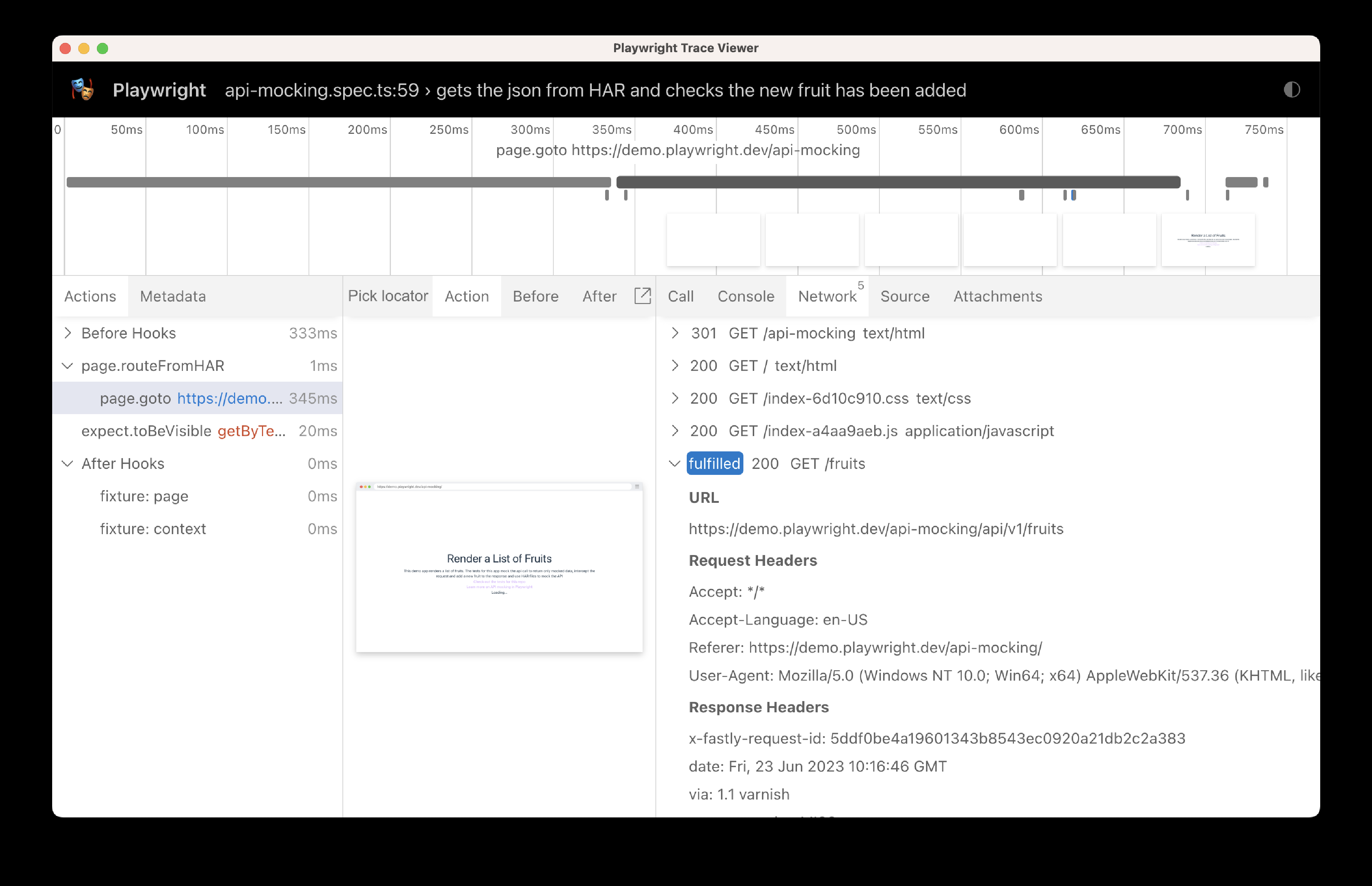
如果我们检查响应,可以看到我们的新水果已被添加到 JSON 中,这是通过手动更新 hars 文件夹内的哈希 .txt 文件完成的。
HAR 重放严格匹配 URL 和 HTTP 方法。对于 POST 请求,它还严格匹配 POST 的有效负载。如果多个录制匹配一个请求,将选择与请求头匹配最多的那一条。任何导致重定向的条目将会自动跟随。
与录制时类似,如果 HAR 文件名以 .zip 结尾,则被视为一个归档文件,包含 HAR 文件和网络负载,负载作为独立条目存储。你也可以提取这个归档文件,手动编辑负载或 HAR 日志,并指向提取出来的 HAR 文件。所有负载将相对于提取的 HAR 文件在文件系统上进行解析。
使用 CLI 录制 HAR 文件
我们推荐使用 update 选项来录制 HAR 文件用于测试。然而,你也可以使用 Playwright CLI 来录制 HAR 文件。
通过 Playwright CLI 打开浏览器,并传递 --save-har 选项来生成 HAR 文件。你还可以使用 --save-har-glob 选项来仅保存你感兴趣的请求,例如 API 端点。如果 HAR 文件名以 .zip 结尾,所有文件将作为独立文件写入并压缩成一个 zip 文件。
# Save API requests from example.com as "example.har" archive.
npx playwright open --save-har=example.har --save-har-glob="**/api/**" https://example.com阅读更多关于高级网络的信息。
模拟 WebSocket
以下代码将拦截 WebSocket 连接并模拟整个 WebSocket 通信,而不是连接到服务器。这个示例将会回应一个 "request" 消息,并返回 "response"。
await page.routeWebSocket('wss://example.com/ws', ws => {
ws.onMessage(message => {
if (message === 'request')
ws.send('response');
});
});另外,你可能希望连接到实际的服务器,但在中间拦截消息并修改或阻止它们。以下是一个示例,它修改了发送给服务器的一些消息,其他消息保持不变。
await page.routeWebSocket('wss://example.com/ws', ws => {
const server = ws.connectToServer();
ws.onMessage(message => {
if (message === 'request')
server.send('request2');
else
server.send(message);
});
});更多详情,请参考 WebSocketRoute 文档。