方法 vs 观察者 vs 计算属性
在 Vue.js 工具箱中,我们可以访问方法、观察者和计算属性。什么时候应该使用其中之一?
方法(method) 最适合用于对 DOM 中发生的事件做出反应,以及在您需要调用函数或执行调用而不是引用值的情况下,例如 date.now()。
在 Vue 中,您可以编写一个由 @click 表示的操作,并引用一个方法:
<template>
<button @click="getDate">Click me</button>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
getDate() {
alert(date.now())
}
}
}
</script>计算属性 最适合在对数据更新做出反应或在模板中为我们编写复杂的表达式时使用。在这种情况下,如果 animalList 数据发生变化,animals 计算属性也将通过从数组中切片第二项并返回新值来更新:
<template>
<div>{{ animals }}</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
animalList: ['dog', 'cat']
}
},
computed: {
animals() {
return this.animalList.slice(1)
}
}
}
</script>它们的响应性质使得计算属性非常适合从现有数据组合新数据变量,例如当您引用更大、更复杂对象的特定键时,有助于简化模板的可读性。在此示例中,我们以两种不同的方式输出作者两次。但是,请注意,在 authorName 计算属性中,您可以干净地编写条件逻辑,而不会导致 HTML 模板膨胀:
<template>
<div>
<p id="not-optimal">{{ authors[0].bio.name }}</p>
<p id="optimal">{{ authorName }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
authors: [
{
bio: {
name: 'John',
title: 'Dr.',
}
}
]
}
},
computed: {
authorName () {
return this.authors ? this.authors[0].bio.name : 'No Name'
}
}
}
</script>当您需要侦听数据(data)属性更改或对象内的特定数据属性,然后执行操作时,应使用数据观察者。由于观察者具有独特的 newVal 和 oldVal 参数,您可以观察变量直到达到某个值,然后才执行操作:
<template>
<div>
<button @click="getNewName()">Click to generate name</button>
<p v-if="author">{{ author }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
data: {},
author: '',
}
},
watch: {
data: function(newVal, oldVal) {
this.author = newVal.first
alert(`Name changed from ${oldVal.first} to ${newVal.first}`)
}
},
methods: {
async getNewName() {
await fetch('https://randomuser.me/api/').
then(response => response.json()).then(data => {
this.data = data.results[0].name
})
},
},
}
</script>考虑到这一点,我们将使用方法、计算属性和观察者构建一个简单的搜索功能,以实现类似的结果并展示每种方法的能力。
练习 2.05:使用 Vue 方法、观察者和计算属性处理搜索功能
在本练习中,您将创建一个组件,允许用户在 Vue 中使用三种不同的方法搜索数据数组。练习结束时,您将能够亲眼目睹每种不同方法的工作原理。
要访问本练习的代码文件,请参阅 https://packt.live/32iDJVe 。
-
打开命令行终端,导航到 Exercise 2.05 文件夹,然后按顺序运行以下命令:
> cd Exercise2.05/ > code . > yarn > yarn serve -
在 data 对象中,在数组中添加框架列表,并分配给 frameworkList 值。包含一个带有 input 键的空字符串和一个带有 methodFilterList 键的空数组:
<script> export default { data() { return { // Shared frameworkList: [ 'Vue', 'React', 'Backbone', 'Ember', 'Knockout', 'jQuery', 'Angular', ], // Method input: '', methodFilterList: [], } }, } </script> -
在模板中,包含一个 div 容器、一个 title 和一个 column 容器。在此 column 容器内,创建一个绑定到 v-model 输入的 input,并将输入上的 keyup 事件绑定到 searchMethod 方法:
<template> <div class="container"> <h1>Methods vs watchers vs computed props</h1> <div class="col"> <input type="text" placeholder="Search with method" v-model="input" @keyup="searchMethod" /> <ul> <li v-for="(item, i) in methodFilterList" :key="i"> {{ item }}</li> </ul> </div> </div> </template> <script> export default { data() { return { // Shared frameworkList: [ 'Vue', 'React', 'Backbone', 'Ember', 'Knockout', 'jQuery', 'Angular', ], // Method input: '', methodFilterList: [], } }, methods: { searchMethod(e) { console.log(e) }, }, } </script> <style lang="scss" scoped> .container { margin: 0 auto; padding: 30px; max-width: 600px; font-family: 'Avenir', Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif; } .col { width: 33%; height: 100%; float: left; } input { padding: 10px 6px; margin: 20px 10px 10px 0; } </style>上述代码的输出如下:
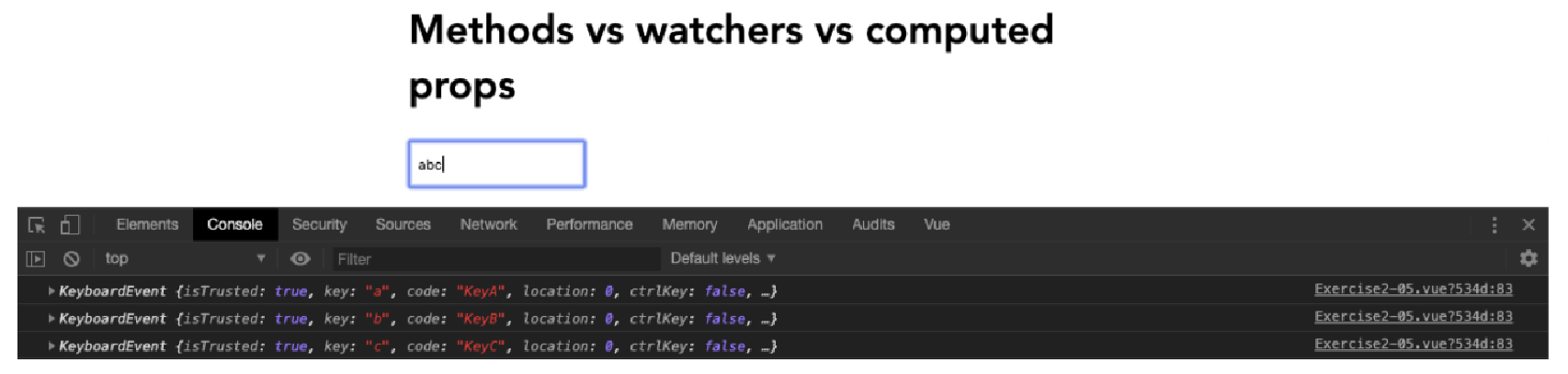 Figure 1. Figure 2.8: Console should output the key input
Figure 1. Figure 2.8: Console should output the key input -
在我们的 searchMethod 方法中,编写一个过滤器表达式,将 methodFilterList 数据属性 绑定到基于输入值的过滤后的 FrameworkList 数组。 在 created() 生命周期钩子上触发 searchMethod,这样当组件加载时,就会出现一个列表:
<script> export default { ... created() { this.searchMethod() }, methods: { searchMethod() { this.methodFilterList = this.frameworkList.filter(item => item.toLowerCase().includes(this.input.toLowerCase())) }, }, } </script>运行上述代码后,您将能够过滤列表,如图 2.9 所示:
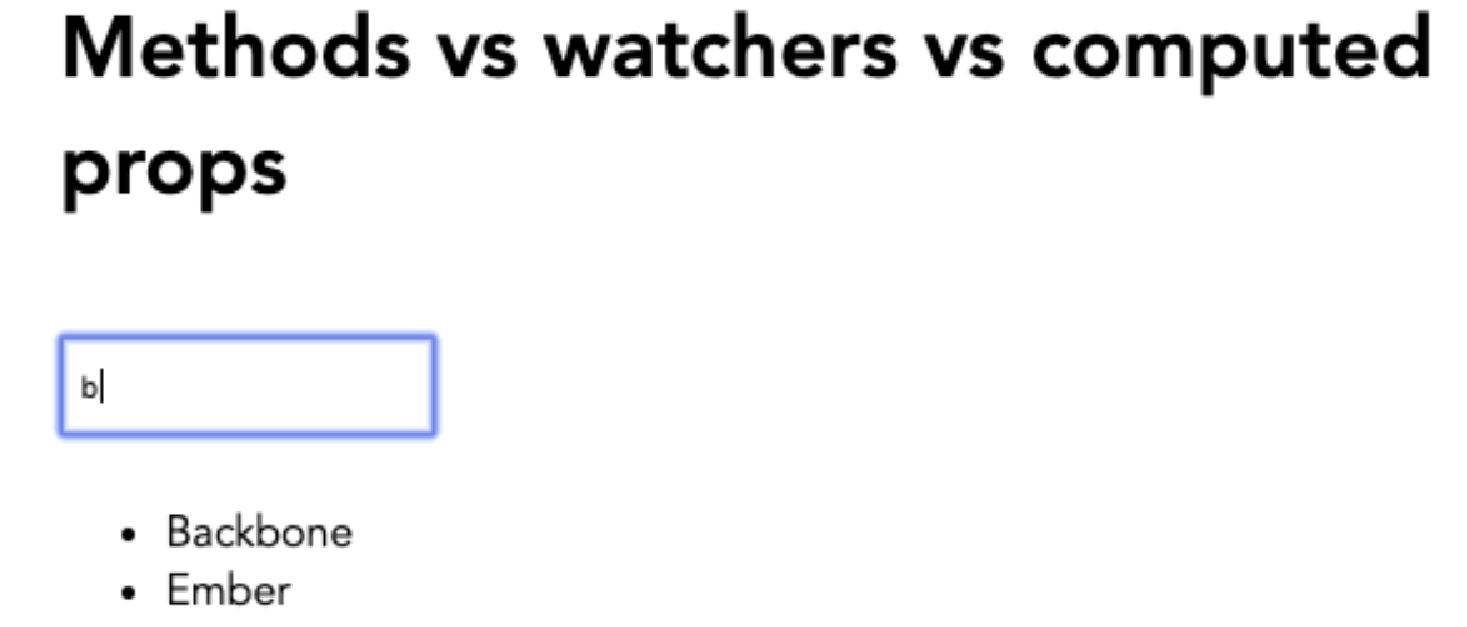 Figure 2. Figure 2.9: You should now be able to filter the list using a Vue method
Figure 2. Figure 2.9: You should now be able to filter the list using a Vue method -
让我们使用计算属性创建一个过滤器。包含一个名为 input2 的新数据属性,并创建一个名为 computeList 的计算属性,它返回与 searchMethod 相同的过滤器,但不需要绑定到另一个数据属性:
<template> <div class="container"> ... <div class="col"> <input type="text" placeholder="Search with computed" v-model="input2" /> <ul> <li v-for="(item, i) in computedList" :key="i">{{ item }}</li> </ul> </div> ... </div> </template> <script> export default { data() { return { ... // Computed input2: '', ... } }, ... computed: { computedList() { return this.frameworkList.filter(item => { return item.toLowerCase().includes(this.input2.toLowerCase()) }) }, }, ... } </script>您现在应该能够借助计算属性来过滤框架的第二列,如以下屏幕截图所示:
 Figure 3. Figure 2.10: Filtering the second column of frameworks using computed props
Figure 3. Figure 2.10: Filtering the second column of frameworks using computed props -
最后,让我们使用观察器过滤相同的列表。包含带有空字符串的 input3 属性和带有空数组的 watchFilterList 属性。还创建第三列 div,其中包含绑定到 input3 v-model 的输入,以及输出 watchFilterList 数组的列表:
<template> <div class="container"> … <div class="col"> <input type="text" placeholder="Search with watcher" v-model="input3" /> <ul> <li v-for="(item, i) in watchFilterList" :key="i">{{ item }}</li> </ul> </div> </div> </template> <script> export default { data() { return { ... // Watcher input3: '', watchFilterList: [], } }, ... </script> -
创建一个观察器,用于观察 input3 属性的更改,并将 FrameworkList 过滤器的结果绑定到 watchFilterList 数组。将 input3 的 immediate 键设置为 true,这样它将在创建组件时运行:
<script> export default { ... watch: { input3: { handler() { this.watchFilterList = this.frameworkList.filter(item => item.toLowerCase().includes(this.input3.toLowerCase())) }, immediate: true, }, }, ... } </script>在观察者的帮助下,您现在应该能够过滤第三列,如以下屏幕截图所示:
 Figure 4. Figure 2.11: Filtering the list using a watcher in the third column
Figure 4. Figure 2.11: Filtering the list using a watcher in the third column
在本练习中,我们了解了如何使用方法、计算属性和观察者来实现过滤列表。每个都有自己的优点、缺点和用例,具体取决于您想要在应用程序中实现的目标。