Prop 类型和验证
Props 定义了 Vue.js 组件的接口。由于 JavaScript 是一种动态类型语言,Vue.js 提供了一个我们可以用来验证 props 的形状和类型的工具。
要验证 prop 类型,应使用对象字面值形式的 props 组件属性(而不是更简单的数组形式)。
基础 Prop 验证
假设我们想要一个带有 times 属性和 content 属性的 Repeat.vue 组件。 我们可以定义以下内容:
<template>
<div>
<span v-for="r in repetitions" :key="r">
{{ content }}
</span>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: ['times', 'content'],
computed: {
repetitions() {
return Array.from({ length: this.times });
}
}
}
</script>我们的 Repeat 组件将按如下方式使用:
<template>
<div id="app">
<Repeat :times="count" content="Repeat." />
<button @click="increment()">Repeat</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Repeat from './components/Repeat.vue'
export default {
components: {
Repeat
},
data() {
return { count: 1 }
},
methods: {
increment() {
this.count += 1
}
}
}
</script>前面的代码将在浏览器中产生以下输出:

单击 Repeat 按钮几次后,Repeat 组件将在每次单击时重复一次,生成输出,如下所示:
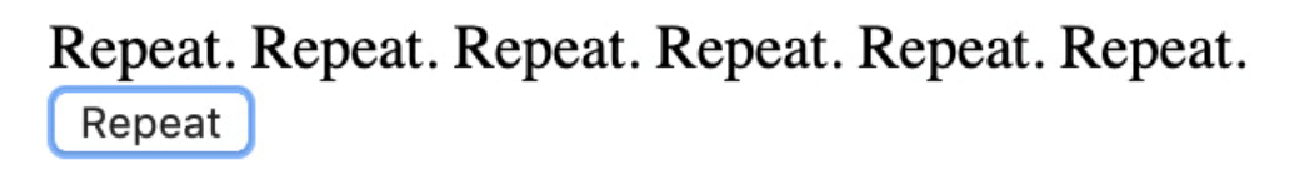
为了让这个组件正常工作,我们需要 times 是一个 Number,并且最好 content 是一个 String。
|
现在是提醒学生 JavaScript 基本类型的好时机:字符串(String)、数字(Number)、布尔值(Boolean)、数组(Array)、对象(Object)、日期(Date)、函数(Function)和符号(Symbol)。 |
Vue.js 支持所有 JavaScript 原始类型构造函数作为 props 字段中的类型提示。
在本例中,我们将 times prop 定义为 Number,将 content prop 定义为 String:
<script>
export default {
props: {
times: {
type: Number
},
content: {
type: String
}
},
// rest of component definition
}
</script>要使用此组件,我们可以更新脚本(script)部分,如下所示:
<script>
import Repeat from './components/RepeatTyped.vue'
// no other changes
</script>在 "happy path" 情况下,为 times 和 content 传递的 props 分别是 Number 和 String,组件的行为仍然相同。
如果我们更新 App,让它故意传递错误类型的 props。在这种情况下,times 是字符串,content 是数字。
<template>
<div id="app">
<Repeat :times="count" :content="55" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
// no changes to imports
export default {
data() {
return { count: 'no-number-here' }
},
// other properties
}
</script>在这里,Repeat 组件将无法渲染,并且以下错误将记录到控制台:
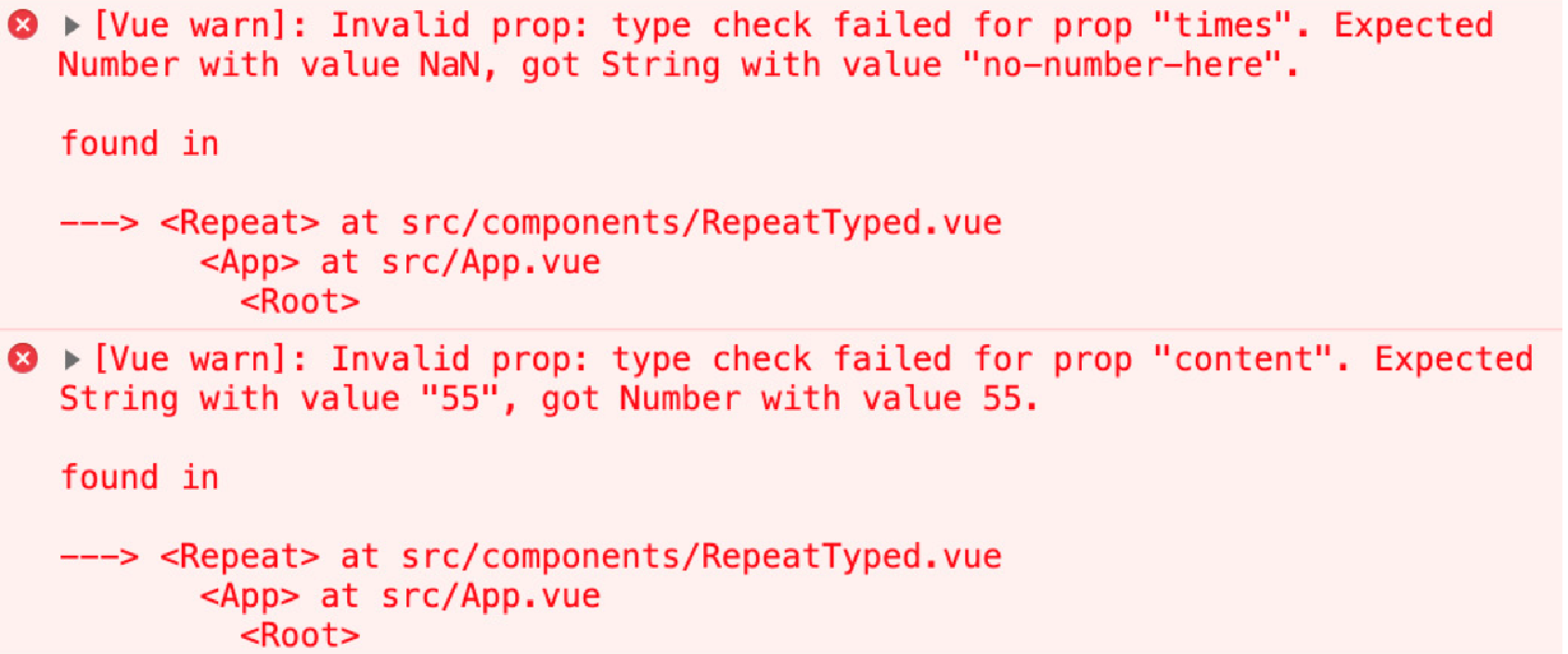
times 属性检查失败,并显示一条消息,解释我们传递了一个字符串作为属性,而该属性应该是一个数字:
Invalid prop: type check failed for prop "times". Expected Number with value NaN, got String with value "no-number-here"content 属性检查失败,并显示一条消息,解释我们传递了一个数字作为属性,而该属性应该是字符串:
Invalid prop: type check failed for prop "content". Expected String with value "55", got Number with value 55|
根据 Vue.js 文档,null 和未定义的值将通过任何类型验证,这意味着类型验证并非万无一失,并且向组件添加自定义验证是有意义的。 |
联合和自定义 Prop 类型
在前面的示例中,我们只是渲染内容,因此内容是什么类型并不重要。
Vue.js 支持联合类型。 联合类型是一种可以是许多其它类型之一的类型。例如,String 或 Number 是联合类型。
Vue.js 中的联合类型使用 prop 的 type 属性的数组来表示,例如,支持数字和字符串作为内容:
<script>
export default {
props: {
// other prop definitions
content: {
type: [String, Number]
}
}
// rest of component definition
}
</script>在这种情况下,我们可以按如下方式使用 RepeatTyped 组件,不会出现错误:
<template>
<div id="app">
<Repeat :times="3" :content="55" />
</div>
</template>这会显示 55 三次。此处,55 作为数字传递,我们的组件现在支持该数字。这可以在以下输出中看到:
55 55 55任何有效的构造函数都可以用作 prop 类型。例如,可以使用 Promise 或自定义 User 构造函数。在下面的示例中,我们定义了一个 TodoList 组件 prop 接口:
<script>
import User from './user.js'
export default {
props: {
todoListPromise: {
type: Promise
},
currentUser: {
type: User
}
}
}
</script>该组件公开的 prop 接口可以按如下方式使用:
<template>
<div>
<template v-if="todosPromise && !error">
<TodoList
:todoListPromise="todosPromise"
:currentUser="currentUser"
/>
</template>
{{ error }}
</div>
</template>
<script>
import TodoList from './components/TodoList.vue'
import User from './components/user.js'
const currentUser = new User()
export default {
components: {
TodoList
},
mounted() {
this.todosPromise = fetch('/api/todos').then(res => {
if (res.ok) {
return res.json()
}
throw new Error('Could not fetch todos')
}).catch(error => {
this.error = error
})
},
data() {
return { currentUser, error: null }
}
}
</script>我们现在已经了解了如何使用联合和自定义类型来验证 Vue.js 属性。
|
Vue.js 在内部使用 instanceof,因此请确保使用相关构造函数实例化任何自定义类型。 传递 null 或 undefined 将使数组和对象的 instanceof 检查失败。 传递数组将通过对象的 instanceof 检查,因为在 JavaScript 中,数组实例也是对象实例。 |
使用验证器对数组、对象形状等进行自定义验证
Vue.js 允许使用 validator 属性将自定义验证器用作 props。 这使我们能够实现有关对象和数组形状的深度检查作为基本类型的自定义逻辑。
为了说明这一点,让我们看一下 CustomSelect 组件。 在基本层面上,select 的 prop 界面包括一系列 options 和一个 selected 的选项。 每个选项都应该有一个代表选择中显示内容的标签和一个与传递给 API 的值相对应的值。例如,所选选项可以为空或应对应于我们选项之一的值字段。
我们的 CustomSelect 可以以简单的方式实现如下(不验证输入):
<template>
<select>
<option
:selected="selected === o.value"
v-for="o in options"
:key="o.value"
>
{{ o.label }}
</option>
</select>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: {
selected: {
type: String
},
options: {
type: Array
}
}
}
</script>然后可以使用 CustomSelect 显示英国脆皮口味(British Crisp flavors)的列表(在 src/App.vue 中):
<template>
<div id="app">
<CustomSelect :selected="selected" :options="options" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
import CustomSelect from './components/CustomSelect.vue'
export default {
components: {
CustomSelect
},
data() {
return {
selected: 'salt-vinegar',
options: [
{
value: 'ready-salted',
label: 'Ready Salted'
},
{
value: 'cheese-onion',
label: 'Cheese & Onion'
},
{
value: 'salt-vinegar',
label: 'Salt & Vinegar'
},
]
}
}
}
</script>前面的应用程序输出一个选择,其中 Salt & Vinegar 是默认选择的选项,如以下屏幕截图所示:

以下屏幕截图显示了三种口味选项,从中选择了一种:

为了进一步验证我们关于形状选项的业务逻辑,我们可以实现以下 prop 验证器:
<script>
export default {
// other component properties
props: {
// other prop definitions
options: {
type: Array,
validator(options) {
return options.every(o => Boolean(o.value && o.label))
}
}
}
}
</script>如果我们传递一个缺少 value 或 label 的选项,我们将在控制台中收到以下消息:
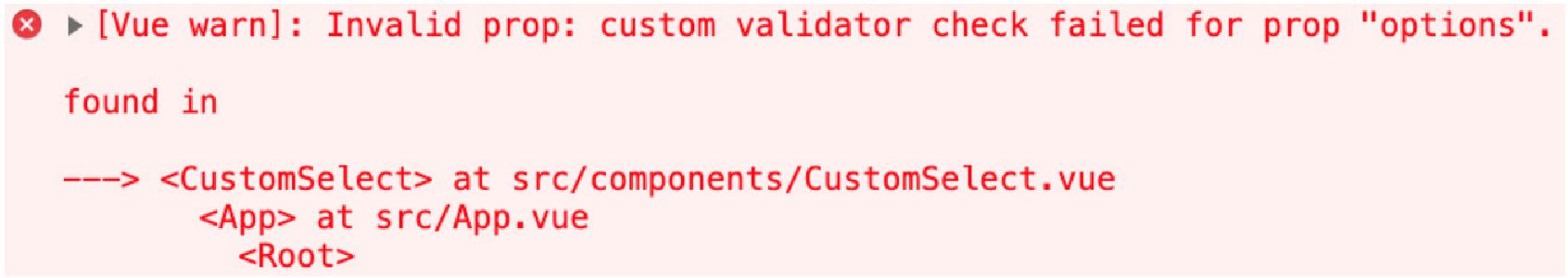
至此,我们学习了如何使用自定义 Vue.js 验证器对复杂的 props 进行深入检查。 接下来,我们将了解 required 的 prop type 属性如何工作。
required Props
要将 Vue.js prop 标记为必需,我们可以使用 required prop type 属性。
在 CustomSelect 示例中,我们可以将 selected 设为必需的 prop。
为此,我们需要修改 prop 定义,使其包含 required:true,如下所示:
<script>
export default {
// other component properties
props: {
selected: {
type: String,
required: true
}
// other prop definitions
}
}
</script>现在,如果我们修改 CustomSelect 的消费者,使其不传递 selected 属性,我们将看到以下错误:
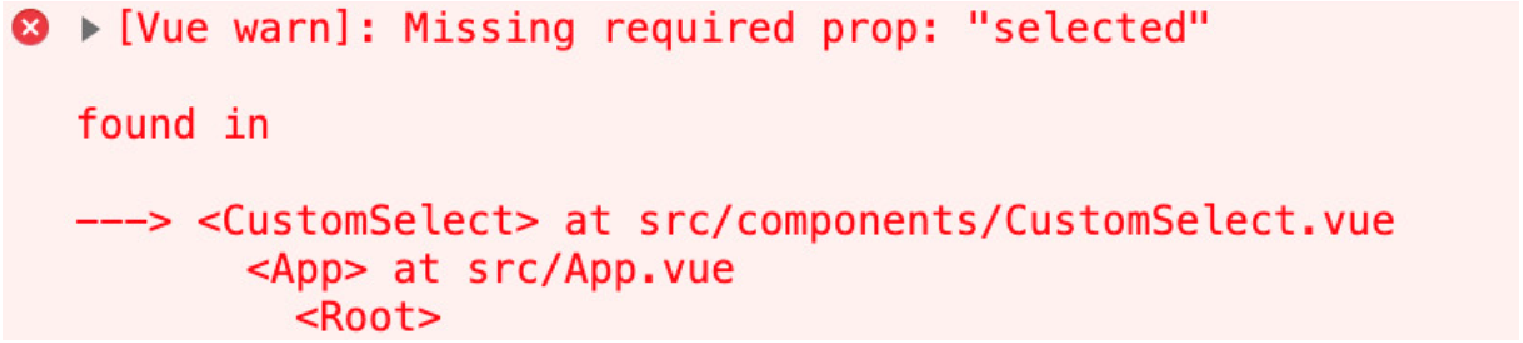
至此,我们学习了如何将 Vue.js props 标记为必需,以及当未传递必需的 props 时会发生什么。接下来,我们将了解默认 props 如何成为最佳选择。
默认 Props
在某些情况下,默认 prop 是组件的最佳接口。
一个例子是 PaginatedList 组件,它接收一个列表,并根据 limit 和 offset 参数显示该列表的子集。在这种情况下,与其设置 limit 和 offset,不如默认 limit 为 25,offset 为 0(默认情况下,我们显示包含 25 个结果的第一页)。
下面就是我们如何实现这样一个没有默认值的 PaginatedList 组件:
<template>
<ul>
<li
v-for="el in currentWindow" :key="el.id"
>
{{ el.content }}
</li>
</ul>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: {
items: {
type: Array
},
limit: {
type: Number
},
offset: {
type: Number
}
},
computed: {
currentWindow() {
return this.items.slice(this.offset, this.limit)
}
}
}
</script>我们可以使用以下代码来使用它:
<template>
<div id="app">
<PaginatedList :items="snacks" :offset="offset" :limit="limit"/>
<button @click="offset++">
Increment Offset (current: {{ offset }})
</button>
<button @click="limit++">
Increment Limit (current: {{ limit }})
</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import PaginatedList from './components/PaginatedList.vue'
export default {
components: {
PaginatedList
},
data() {
return {
offset: 0,
limit: 0,
snacks: [
{
id: 'ready-salted',
content: 'Ready Salted'
},
{
id: 'cheese-onion',
content: 'Cheese & Onion'
},
{
id: 'salt-vinegar',
content: 'Salt & Vinegar'
},
]
}
}
}
</script>通过将 limit 增加到 3,我们可以显示整个列表,如下所示:
Hello Vue.js然后,通过增加偏移量,我们可以跳过列表中的前 X 个元素。以下屏幕截图显示了 PaginatedList:
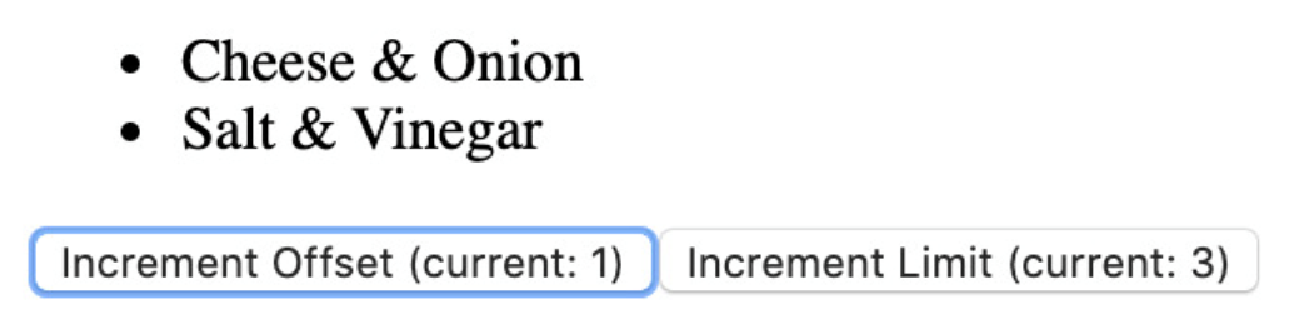
现在,为了使我们的 PaginatedList 具有弹性,我们将默认限制为 25,偏移量为 0。为此,我们可以设置相关 props 的默认(default)属性值:
<script>
export default {
props: {
// other props
limit: {
type: Number,
default: 25,
},
offset: {
type: Number,
default: 0,
}
},
// other component properties
}
</script>使用这些默认值,我们将默认显示列表开头的 25 个项目。
根据 Vue.js 文档,在数组和对象的情况下存在默认值的问题(例如,如果我们想要默认项); 也就是说,“对象或数组默认值必须从工厂函数返回”。
工厂函数是一个函数(在本例中称为 default),它返回我们想要的默认值。
对于项目,我们可以写如下:
<script>
export default {
props: {
items: {
type: Array,
default() {
return []
}
}
// other props
},
// other component properties
}
</script>这样,我们就学会了如何设置 Vue.js 组件 props 默认值。当我们希望为可选参数提供值时,这会很有帮助,以便 Vue.js 组件实现不需要处理默认的 prop 值。
练习 4.03:验证对象属性
在本练习中,我们将重写 Repeat 组件,使其支持用于传递 times(数字)和 content(字符串)的单个 config 属性。
我们必须编写一个自定义验证器来确保 times 和 content 存在并且类型正确。
要访问本练习的代码文件,请参阅 https://packt.live/2Ui1hVU 。
请按照以下步骤完成本练习:
-
我们希望我们的 src/components/Repeat.vue 组件支持 config prop。 这将是一个生成以下 <script> 的对象:
<script> export default { props: { config: { type: Object } } } </script> -
接下来,我们希望在传递配置(config)时渲染一些内容。为此,我们将通过计算属性创建一个
v-for数组。数组长度将基于config.times的值:<script> export default { // other component properties computed: { repetitions() { return Array.from({ length: this.config.times }) } } } </script> -
下一步是设置 <template> 以便它为每个 repetitions 项渲染 config.content:
<template> <div> <span v-for="r in repetitions" :key="r"> {{ config.content }} </span> </div> </template> -
目前,我们正在确保 content 和 times 已设置且类型正确。为此,我们将在 config prop 的验证器中实现 typeof 检查:
<script> export default { props: { config: { type: Object, validator(value) { return typeof value.times === 'number' && typeof value.content === 'string' } } }, // other component properties } </script> -
最后,我们可以从 src/App.vue 中使用 Repeat。我们需要导入它,注册它(在脚本(script)中),然后在模板(template)中渲染它:
<template> <div id="app"> <Repeat :config="{}" /> </div> </template> <script> import Repeat from './components/Repeat.vue' export default { components: { Repeat } } </script>不幸的是,这不会渲染任何内容,因为 config 是一个空对象。您将看到一条警告,如下所示:
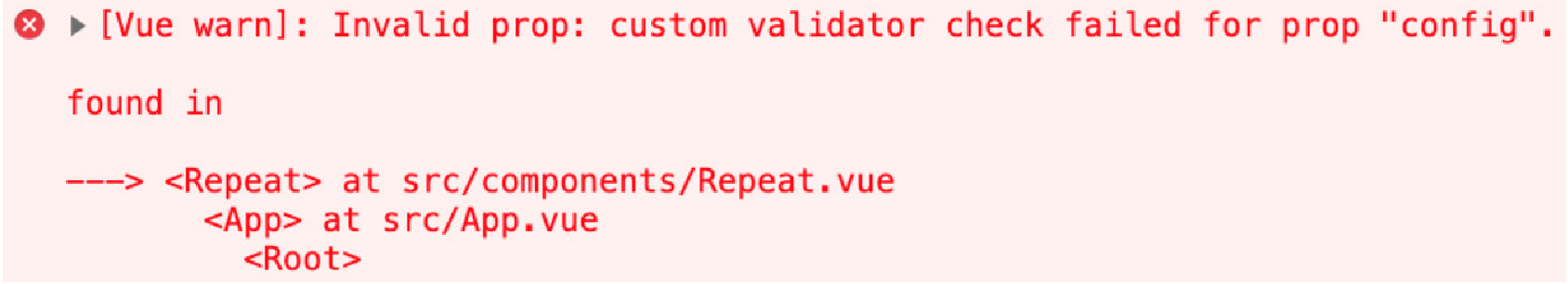 Figure 9. Figure 4.15: Vue.js warning due to the config prop’s custom validator check failing
Figure 9. Figure 4.15: Vue.js warning due to the config prop’s custom validator check failing在以下情况下我们会看到同样的错误:
-
我们只添加 times 属性;即
<Repeat :config="{ times: 3 }" />。 -
我们只添加一个 content 属性; 即
<Repeat :config="{ content: 'Repeat me.' }" />。 -
times 类型错误; 即
<Repeat :config="{ times: '3', content: 'Repeat me.' }" />。 -
content 的属性类型错误; 即
<Repeat :config="{ times: 3, content: 42 }" />。
-
-
为了使 Repeat 正常工作,我们可以将模板(template)中使用它的行修改为以下内容:
<Repeat :config="{ times: 3, content: 'Repeat me.' }" />这在控制台中显示没有错误并呈现 "Repeat me"。 共三次,如下:
Repeat me. Repeat me. Repeat me.
至此,我们展示了如何验证 props 以更好地定义 Vue.js 组件的接口。
接下来是对槽(slots)的深入研究,槽是我们可以用来通过推迟模板逻辑来组合组件的机制。